AI watermarking is a powerful way to protect digital content from misuse and ensure ownership is traceable. Unlike traditional watermarks, AI watermarking embeds invisible markers directly into images, text, audio, or video during their creation. These markers are resistant to editing, cropping, and compression, making them harder to remove. They also help identify machine-generated content and provide proof of authorship.
Key Points:
- How It Works: AI watermarking integrates markers at the model level, leaving statistical or pixel-level signatures that are invisible to users but detectable with specialized tools.
- Detection: Algorithms and cryptographic methods verify watermarks while maintaining accuracy, even after content is altered.
- Blockchain Integration: Blockchain adds an extra layer of security, recording ownership and ensuring tamper-proof verification.
- Benefits: Protects against content misuse, supports legal claims, and works across diverse media types like text, images, and videos.
- Challenges: Risks include watermark removal, false positives, and lack of universal detection standards.
With an estimated market value of $535.1 million in 2025, AI watermarking is becoming a key tool for copyright protection. Platforms like ScoreDetect combine watermarking with blockchain and automated monitoring to safeguard digital assets effectively.
Stopping Piracy and Deepfakes at Once
sbb-itb-738ac1e
How AI-Driven Invisible Watermarking Works
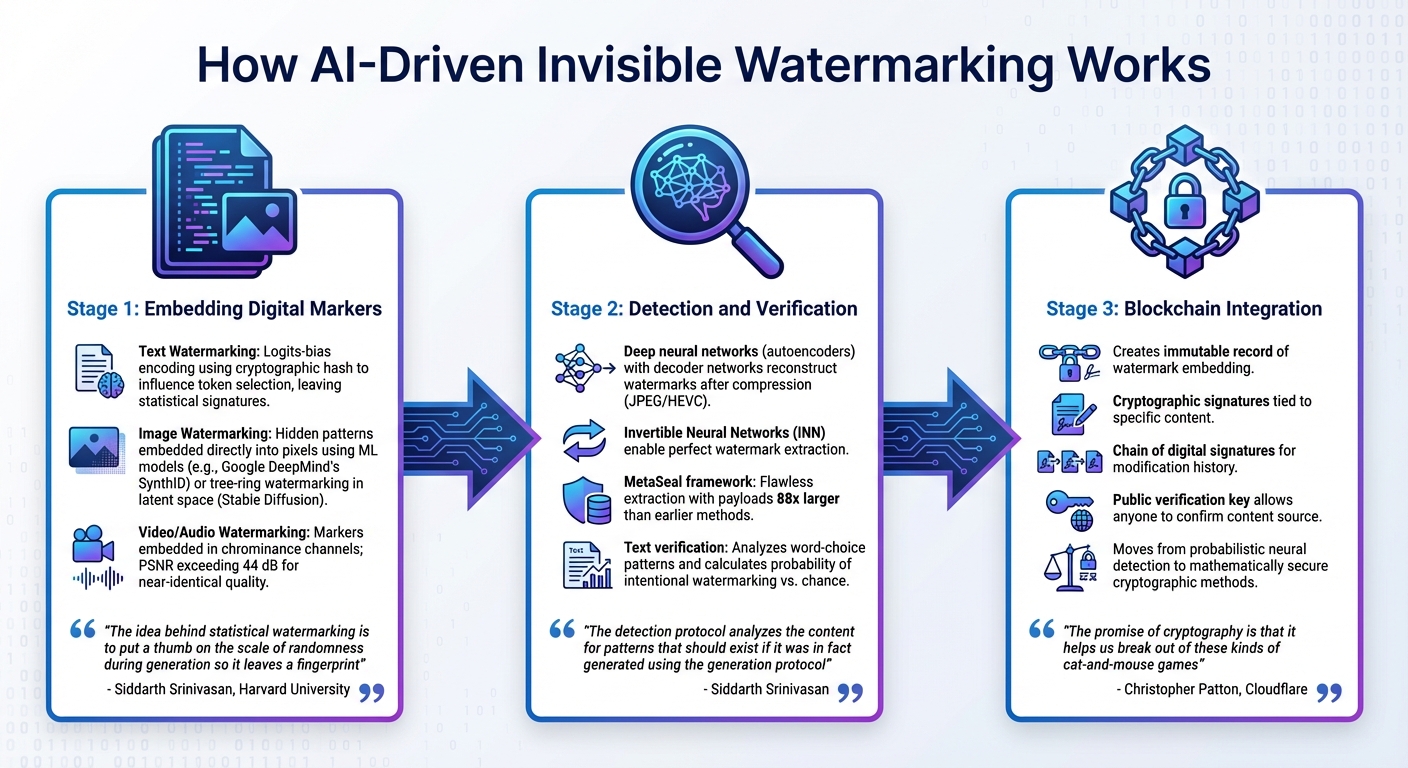
How AI Watermarking Works: Embedding, Detection, and Blockchain Verification
AI-driven invisible watermarking embeds hidden markers directly into digital content during its creation or processing. Unlike traditional watermarks added later, this technique integrates at the model level, making it much harder to remove or manipulate.
Embedding Digital Markers
The way markers are embedded depends on the type of content. For text, AI models use a method called logits-bias encoding. This involves a cryptographic hash that sorts tokens into two groups, subtly influencing token selection to leave a statistical signature without affecting how the text reads[2][8].
"The idea behind statistical watermarking is to put a thumb on the scale of randomness during generation so it leaves a fingerprint that can be detected later", explains Siddarth Srinivasan, Postdoctoral Fellow at Harvard University[4].
For images, tools like Google DeepMind‘s SynthID (introduced in August 2023) embed hidden patterns directly into the pixels using a secondary machine learning model[4][1]. Another technique, called tree-ring watermarking, places signals in the initial random noise (latent space) before the image is generated in systems like Stable Diffusion[4]. In video and audio, markers are embedded in chrominance channels, which minimizes visible color shifts. Advanced video watermarking methods using deep neural networks achieve a Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) exceeding 44 dB, ensuring the watermarked content looks nearly identical to the original[5].
Once these invisible markers are in place, the next step is to detect and verify them to confirm the content’s authenticity.
Detection and Verification
Specialized machine learning algorithms are used to detect the embedded markers. Deep neural networks, often acting as autoencoders, include a decoder network that can reconstruct the watermark even after the content has been compressed (e.g., through JPEG or HEVC)[5]. Invertible Neural Networks (INN) enhance this process by enabling perfect watermark extraction using the same architecture for embedding and retrieval[3]. Frameworks like MetaSeal can achieve flawless extraction with payloads 88 times larger than earlier methods[3].
"The detection protocol analyzes the content for patterns that should exist if it was in fact generated using the generation protocol", notes Siddarth Srinivasan[4].
For text, verification involves calculating how likely it is that observed word-choice patterns happened by chance, as opposed to being a result of intentional watermarking. In January 2023, OpenAI researcher Scott Aaronson developed a prototype for large language models that used a cryptographic function to bias word choices, embedding a hidden signature verifiable with a private key[2][4].
Integration with Blockchain Technology
To strengthen detection efforts, watermarking systems are now integrating with blockchain technology. Blockchain creates an immutable record of watermark embedding by tying cryptographic signatures to specific content. This establishes a chain of digital signatures, with each link representing a modification to the content. It provides a verifiable ownership history[6]. By moving from probabilistic neural network detection, which can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, to mathematically secure cryptographic methods, this approach ensures unforgeability[6][3].
"The promise of cryptography is that it helps us break out of these kinds of cat-and-mouse games", says Christopher Patton of Cloudflare[6].
Embedding cryptographic markers ensures that records of origin persist even after reformatting or modification[6][3]. With a public verification key, anyone can confirm the source of the content. This makes the approach especially valuable for copyright enforcement and legal disputes[2][3].
Benefits of AI Watermarking for Copyright Protection
AI watermarking has become a powerful tool for digital content protection in an era of massive content creation. By embedding unique identification markers directly into digital files, watermarking helps trace ownership and verify authenticity on a large scale. This technology not only deters misuse but also strengthens creators’ legal rights while offering seamless protection across various types of media.
Preventing Content Misuse
Invisible watermarks play a critical role in discouraging unauthorized use and redistribution. These markers are designed to withstand common alterations like cropping, blurring, or rotation, making it much harder for anyone to repurpose content undetected. For example, a 2023 poll conducted across 17 countries revealed that 71% of participants were concerned about AI-driven scams and impersonation[1]. Watermarks act as digital signatures, allowing creators to prove ownership and authorship with confidence.
Supporting Legal Claims
When it comes to copyright disputes, AI watermarks provide solid, forensic-level evidence that goes beyond traditional metadata, which can be easily removed[9].
"To best fulfill its purpose, a watermark should be able to withstand forensic verification. That means without any doubt the watermark is there, could not have been caused by chance, and will hold up in whatever court jurisdiction is necessary", explains Access Now[9].
Modern watermarking methods use cryptographic signatures to create a secure, unbreakable link between the content and its creator. Techniques like Invertible Neural Networks (INN) ensure precise extraction of watermarks, further bolstering the reliability of this evidence. As TechTarget highlights:
"AI watermarks serve as digital signatures that can demonstrate provenance, or the origin of a piece of media. This could be useful in contexts such as scientific investigations or legal proceedings, where research findings or evidence could be scanned for AI watermarks to evaluate their integrity", notes TechTarget[2].
By moving away from detector-based verification – which can be vulnerable to adversarial attacks – toward cryptographic methods, watermarking provides a clear "proven/not proven" result. This approach directly addresses the risk of the "liar’s dividend", where genuine human-created content could be falsely labeled as AI-generated.
Scalability Across Different Media Types
AI watermarking is versatile, working effectively across images, videos, audio, and documents. For instance, advanced techniques for HEVC video compression allow robust embedding of 96 bits per 128×128 frame, ensuring detectability even after significant compression or data reduction[5]. Thanks to cloud-based solutions, this scalability is further enhanced. By 2025, cloud-based watermarking is expected to make up 73% of the market[7]. This integration into existing workflows enables real-time monitoring and protection, ensuring digital assets remain secure across global platforms.
ScoreDetect‘s AI Watermarking Solution
ScoreDetect takes the watermarking techniques discussed earlier and transforms them into a practical, scalable system for copyright protection. By combining invisible watermarking, automated content monitoring, and blockchain verification, the platform safeguards digital content for a range of industries. It covers every stage of content protection – from embedding watermarks to detecting misuse and managing takedown actions.
Invisible Watermarking Across Media Types
To maintain content integrity, ScoreDetect embeds invisible, non-intrusive watermarks into images, videos, audio, and documents without affecting their quality. This is done by subtly altering pixel values or embedding inaudible signals that can only be read by specialized tools[10]. Invisible watermarking is quickly becoming the industry standard, and it’s projected to account for 61% of the market share by 2025[7].
The watermarks applied by ScoreDetect are built to withstand common alterations like cropping, resizing, and compression, ensuring that ownership remains verifiable over time.
Automated Content Monitoring and Takedown
ScoreDetect operates around the clock, using advanced web scraping technology to monitor the internet for unauthorized use of watermarked content. Impressively, this system bypasses most preventative measures with a 95% success rate. It scans everything from commercial websites to broader online platforms to identify matches for your protected content[12].
When an infringement is detected, the platform automatically verifies the watermark, retrieves ownership details, and issues takedown notices. These notices achieve a takedown rate of over 96%, streamlining what would otherwise be a time-consuming, manual process. This automation makes it easier to scale content protection efforts without additional resources.
Blockchain Timestamping and SEO Integration
ScoreDetect uses blockchain technology to create a secure, tamper-proof timestamp for your content. By capturing a checksum rather than storing the actual files, it establishes a reliable audit trail that can strengthen your position in copyright disputes[11].
The platform also offers a WordPress plugin that automatically generates blockchain-verified ownership certificates for every article you publish or update. These certificates not only confirm ownership but also enhance SEO by aligning with search engine preferences for metadata transparency, building trust with both users and algorithms[10].
For users on the Pro plan, ScoreDetect provides 100 new verifiable certificates each month, along with unlimited content protection and revision history, starting at $11.31 per month when billed annually. For businesses needing more robust solutions, the Enterprise plan includes all features, plus white labeling, a dedicated success manager, and 24×7 premium support to meet enterprise-level demands.
Challenges and Limitations of AI Watermarking
AI watermarking plays a key role in protecting copyrights, but it’s not without its flaws. Recognizing these challenges can help you decide how to best implement watermarking systems and manage expectations about their capabilities.
Risks of Watermark Removal
Attackers have become increasingly skilled at removing watermarks from protected content. One of the most concerning methods is regeneration attacks, where noise is added to erase pixel-level watermarks. Afterward, diffusion models or denoising algorithms reconstruct the image, effectively stripping the watermark away.
Another major issue is forgery and misattribution. Fixed-pattern watermarks, which are not tied to specific content, can be copied from one image and applied to unrelated material. These "replay attacks" can falsely attribute harmful content to a particular creator or AI model, leading to reputational damage.
Detection systems also face manipulation risks. For example, neural network-based detectors can fall victim to Projected Gradient Descent (PGD) attacks, where subtle, nearly invisible changes trick the system into producing false results. Similarly, text-based watermarks can be bypassed with simple paraphrasing techniques.
To counter these threats, ScoreDetect employs content-dependent watermarking, which uses semantic features to make watermarks harder to remove or transfer. Additionally, its blockchain integration provides cryptographic verification, offering a tamper-proof way to confirm ownership without relying on external systems.
But technical vulnerabilities are just one piece of the puzzle. Broader issues like regulation and compatibility further complicate the adoption of watermarking technologies.
Regulatory and Interoperability Concerns
One of the biggest obstacles in watermarking is lack of universal detection standards. Detectors are typically proprietary, meaning they can only identify watermarks created by their own developers. This forces platforms to check content against multiple detection protocols, creating a time-consuming and expensive process that discourages widespread adoption[4].
Adding to the complexity is regulatory uncertainty. With legal frameworks evolving rapidly, companies hesitate to invest in specific solutions, fearing that today’s tools may not comply with tomorrow’s rules. Open-source models exacerbate this issue by allowing users to remove watermarking code, undermining compliance efforts[4][9].
Privacy concerns also come into play. Mandated watermarks that track user identities can conflict with privacy rights. As Sam Gregory, Executive Director of WITNESS, explains:
"People using generative AI tools to create audiovisual content should not be required to forfeit their right to privacy to adopt these emerging technologies"[9].
For instance, mandatory labeling could expose whistleblowers or suppress dissent. It might also unfairly impact neurodivergent individuals who rely on AI tools for accessibility.
ScoreDetect addresses these concerns by focusing on content protection rather than user identification. Through blockchain-based timestamps, the platform creates secure ownership records without storing sensitive digital assets. Its integration with over 6,000 web apps via Zapier ensures broad compatibility, simplifying workflows across different systems.
Even with these solutions, detection accuracy remains a pressing issue.
False Positives and Accuracy
Achieving reliable detection is a persistent challenge. A false positive rate as small as 1% can undermine practical uses like spam filtering or verifying educational content[4]. False positives might wrongly flag human-created work as AI-generated, while false negatives allow unauthorized content to slip through undetected.
A promising solution lies in cryptographic verification, which goes beyond simple pattern recognition. Instead of just identifying watermarks, this method validates whether a specific digital signature is embedded in the content. As Tong Zhou and researchers at Northeastern University note:
"To escape the forgery trap, the reliable attribution requires both content-dependent watermarking and cryptographic verification guarantees, with the attribution information being self-contained and provable"[3].
In September 2025, researchers from Northeastern University, Cisco, and UC Riverside introduced MetaSeal, a framework that demonstrated perfect accuracy in extracting payloads 88 times larger than previous methods. By leveraging an invertible neural network and cryptographic signatures, MetaSeal effectively blocked forgery attacks that often bypass conventional AI detectors[3].
Statistical probability thresholds also help reduce false positives. Siddarth Srinivasan, Postdoctoral Fellow at Harvard University, explains:
"The detection protocol can compute the probability of producing the observed patterns in the content without the generation protocol, purely by chance. The lower the chance, the more confident we can typically be"[4].
ScoreDetect tackles accuracy issues with a multi-step verification process. It starts by identifying potential matches using web scraping, then cross-checks watermarks against blockchain records before issuing takedown notices. This comprehensive approach has resulted in a 96% takedown success rate, balancing robust enforcement with minimal errors. By combining multiple verification layers, ScoreDetect effectively addresses the challenges of detection accuracy.
Conclusion
AI-driven invisible watermarking has become a key tool for safeguarding digital content in a world flooded with AI-generated images and synthetic media [1]. Unlike older methods that rely on metadata – which can easily be stripped during file transfers – these invisible watermarks embed attribution directly into the content. They remain intact even after cropping, compression, or standard editing [3][11].
Today’s AI watermarking solutions offer high-quality results while providing reliable forensic evidence. This helps deter copyright violations under the DMCA, which carries hefty financial penalties [5][14]. The growing recognition of this technology is reflected in the market’s trajectory, valued at $535.1 million in 2025 and expected to soar to $5,104.4 million by 2035 [7].
That said, watermarking alone isn’t enough. As Chakraborty et al. emphasize, any effective solution must strike a balance – offering proof of ownership while still allowing the "free sharing of digital content" [13]. Achieving this balance requires a layered approach. Combining invisible watermarks with blockchain timestamping ensures tamper-proof verification, while automated monitoring tools can track and flag unauthorized use online.
Platforms like ScoreDetect are already putting these technologies into action. ScoreDetect streamlines the entire protection process, from watermarking to issuing takedown notices. Its blockchain integration creates secure ownership records without storing sensitive assets, and its WordPress plugin adds an extra layer of security by automatically protecting published content while boosting SEO.
FAQs
What makes AI watermarking different from traditional methods?
AI watermarking embeds an invisible, machine-readable signal into AI-generated content – be it text, images, audio, or video – right at the time of creation. This signal is designed to stay hidden from human eyes, withstand common edits, and trace the content back to its source. It allows AI-generated material to be identified without affecting its overall quality.
In contrast, traditional watermarking adds visible elements like logos or overlays, or hidden metadata, to a finished piece. These marks are often static, easier to modify or erase, and mainly serve to establish ownership rather than confirm AI origin. AI watermarking takes things further by using advanced cryptographic methods to resist tampering and provide verifiable proof of origin – something traditional watermarking methods typically don’t offer.
How does blockchain improve the security of AI watermarking?
Blockchain technology boosts the security and trustworthiness of AI-powered invisible watermarks by introducing a tamper-resistant layer of verification. By storing a cryptographic checksum of the watermarked content on an unchangeable ledger, it allows the watermark’s origin to be confirmed without revealing the actual content. This makes it possible to detect any attempts to modify or erase the watermark.
ScoreDetect leverages this approach by recording a unique checksum for every piece of content directly on the blockchain. This creates a reliable proof of ownership that can be used in takedown notices or audit trails, reinforcing copyright protection while ensuring your original digital assets remain confidential.
What challenges and limitations does AI watermarking face?
AI watermarking shows promise but comes with several hurdles that affect its reliability as a tool for copyright protection.
One major issue is that invisible watermarks are susceptible to removal using advanced techniques, such as adding noise or employing AI-driven image reconstruction. These methods can erase watermarks without noticeably altering the content, making it tough to ensure lasting protection. Compounding this, many watermarking systems are content-agnostic – they use the same hidden pattern repeatedly. If leaked, these patterns could be misused by forgers to embed them into counterfeit material, creating false claims of ownership.
Another significant challenge lies in balancing invisibility and robustness. Watermarks that are too subtle may not withstand transformations like cropping, compression, or color adjustments. On the other hand, stronger, more noticeable watermarks compromise their imperceptibility, defeating the purpose. Striking the right balance while preserving the quality of the original content is a complicated task. These challenges underscore why AI watermarking remains a work in progress rather than a foolproof solution.

