Medical images like X-rays and MRIs are critical for patient care but are increasingly at risk of tampering and data breaches. Current watermarking methods often degrade image quality or rely on centralized systems that can fail. Blockchain offers a decentralized, secure solution to these challenges by:
- Ensuring image integrity: Cryptographic hashes detect any changes to the image.
- Tracking access and ownership: A permanent, tamper-proof ledger records every interaction.
- Improving security: Decentralized verification prevents single points of failure.
- Maintaining diagnostic quality: Advanced methods preserve image clarity (e.g., PSNR values over 60 dB).
Blockchain also enables encrypted watermarks, timestamping for proof of existence, and seamless integration with AI systems, ensuring medical images remain secure, traceable, and high-quality.
Blockchain Fundamentals for Medical Image Watermarking
Decentralized Ledgers for Image Verification
Blockchain’s decentralized nature offers a powerful tool for securing and verifying medical images. It functions as a distributed ledger that records data permanently across multiple nodes, making it nearly impossible for any single entity to alter the information without detection. In the context of medical image watermarking, this ensures that hospitals, researchers, and data scientists can confirm an image’s authenticity without depending on centralized oversight [2].
"Blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that saves information to make sure that it will remain the same and not be changed by anyone." – Alsehli Abrar, Department of Computer Engineering, King Saud University [2]
When a medical image undergoes watermarking, cryptographic hashes of both the original and watermarked versions are stored on the blockchain. Each node in the network holds a copy of this ledger, making unauthorized tampering virtually impossible. If someone tries to modify an image, the hash will no longer match the blockchain record, immediately signaling a discrepancy [4].
This decentralized setup creates a secure log for every watermarking event. Each action – whether it’s watermarking, extraction, or verification – is recorded with a unique timestamp. For instance, in June 2025, the European project PAROMA-MED showcased this technology by using a private blockchain to track over 544,000 lung X-ray images across multiple data centers. This enabled researchers to train AI models while maintaining full traceability of image access [4]. The next layer of security is achieved by combining cryptographic hashing with smart contracts, which further automate and strengthen these processes.
Cryptographic Hashing and Smart Contracts
SHA-256 hashing plays a key role in securing medical images. It generates a unique 256-bit fingerprint for each image, ensuring that even if someone accesses the blockchain, the original content remains protected [2]. Smart contracts streamline the verification process by automating workflows, reducing human error, and eliminating the need for third-party involvement. In advanced systems, encrypted watermarking parameters and secret keys are stored on the blockchain, ensuring that only authorized users can remove watermarks or validate ownership. Digital signatures authenticate each operation, while lightweight CNN decoders (just 0.65 MB) achieve watermark extraction accuracies exceeding 99% [5][4].
These technologies also enable robust timestamping, offering additional proof of an image’s integrity and history.
Blockchain Timestamping for Proof of Existence
Blockchain timestamps provide an immutable record of when a medical image was watermarked or accessed. This temporal evidence is critical in resolving ownership disputes and establishing the sequence of events in collaborative healthcare environments [9].
Unlike traditional Time Stamping Authorities (TSAs), blockchain eliminates single points of failure. Once a timestamp is added to the ledger, it becomes a permanent record that cannot be altered or erased, offering indisputable proof that an image existed at a specific time [9]. This feature was vital in the PAROMA-MED project, where researchers tracked the lifecycle of medical images as they moved between data providers and AI training systems.
"Based on the watermark, it becomes possible to interrogate the blockchain about the life cycle of an image to ensure data traceability, authenticity, and integrity." – Reda Bellafqira, IMT Atlantique [4]
How Blockchain Strengthens Medical Image Watermarking
Encrypted Watermarks with Blockchain Verification
Blockchain technology offers a robust way to secure medical image watermarks by combining encryption with decentralized verification. Here’s how it works: the watermark content is encrypted using AES-128, and a SHA-256 hash of this encrypted watermark is stored on the blockchain ledger. This system ensures both security and authenticity for medical images [2].
A study conducted in February 2021 by King Saud University showcased this approach using the Ethereum blockchain and the MedPix medical image database. The researchers encrypted watermark IDs with AES-128 and stored their SHA-256 hashes on the blockchain. The results? Exceptional image quality with PSNR values reaching 54.899 dB, and verified image authenticity without the need for a trusted third party [2].
"The proposed medical image watermarking approach is the first method that demonstrates an effective solution to the medical image authentication problem using the blockchain, thus removing the need for trusted third parties."
– Alsehli Abrar et al., King Saud University [2]
By eliminating the reliance on centralized systems, this decentralized method avoids the vulnerabilities of single points of failure [2, 5].
Resistance to Attacks Through Blockchain
Blockchain-backed watermarking also proves highly resistant to image manipulation. Tests on Ethereum-based systems revealed that even after JPEG compression at 90%, the watermark maintained a PSNR of 38.469 dB and a Normalized Correlation (NC) of 0.994, ensuring the watermark’s integrity and verifiability [2].
In June 2025, IMT Atlantique proposed a framework for Federated Learning systems that used a private blockchain to store cryptographic hashes of original and watermarked chest X-ray images alongside encrypted parameters. This setup allowed data scientists to trace the entire lifecycle of an image without disrupting the training of VGG-16 AI models. The project also demonstrated that GAN-based methods for embedding patient-specific QR codes achieved extraction accuracy exceeding 99% [5, 6].
To further enhance reliability, majority voting schemes embed watermarks in multiple regions of an image. During extraction, consensus among these instances significantly lowers the Bit Error Rate, even if parts of the image are damaged [4].
These advanced techniques pave the way for practical applications, such as ScoreDetect, which uses blockchain timestamping to secure medical images.
Case Study: ScoreDetect‘s Blockchain Timestamping
Maintaining an unbroken chain of custody is critical in medical imaging, especially for legal and compliance purposes. ScoreDetect addresses this need by applying blockchain timestamping to protect digital assets. Instead of storing actual files, the platform records a cryptographic fingerprint (checksum) on the blockchain. This creates verifiable proof of existence and ownership while safeguarding privacy and reducing storage costs.
For healthcare providers, ScoreDetect offers a seamless way to establish immutable audit trails. Every time a medical image is created or modified, the system generates a verification certificate containing the SHA-256 hash, registration date, and blockchain transaction URL. This certificate can serve as legal evidence during disputes or audits.
The platform’s flexibility is impressive. It integrates with over 6,000 web apps via Zapier, enabling automation of content protection workflows. For instance, a radiology department can set up automatic timestamping for every new diagnostic image uploaded to their PACS system. ScoreDetect also offers a WordPress plugin that captures and timestamps every published article or image, providing proof of ownership and boosting SEO by enhancing E-E-A-T signals.
With a certificate generation time of about 3 seconds, the service is ideal for high-volume environments. Healthcare providers can start with the Pro plan at $11.31 per month (billed annually), which includes 100 certificates per month and unlimited content protection. For larger-scale needs, enterprise plans offer additional features like invisible watermarking for images, videos, and audio, as well as automated takedown notifications with a success rate exceeding 96%.
Encryption based Watermarking Technique for Security of Medical Image
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Benefits of Blockchain-Based Watermarking for Healthcare
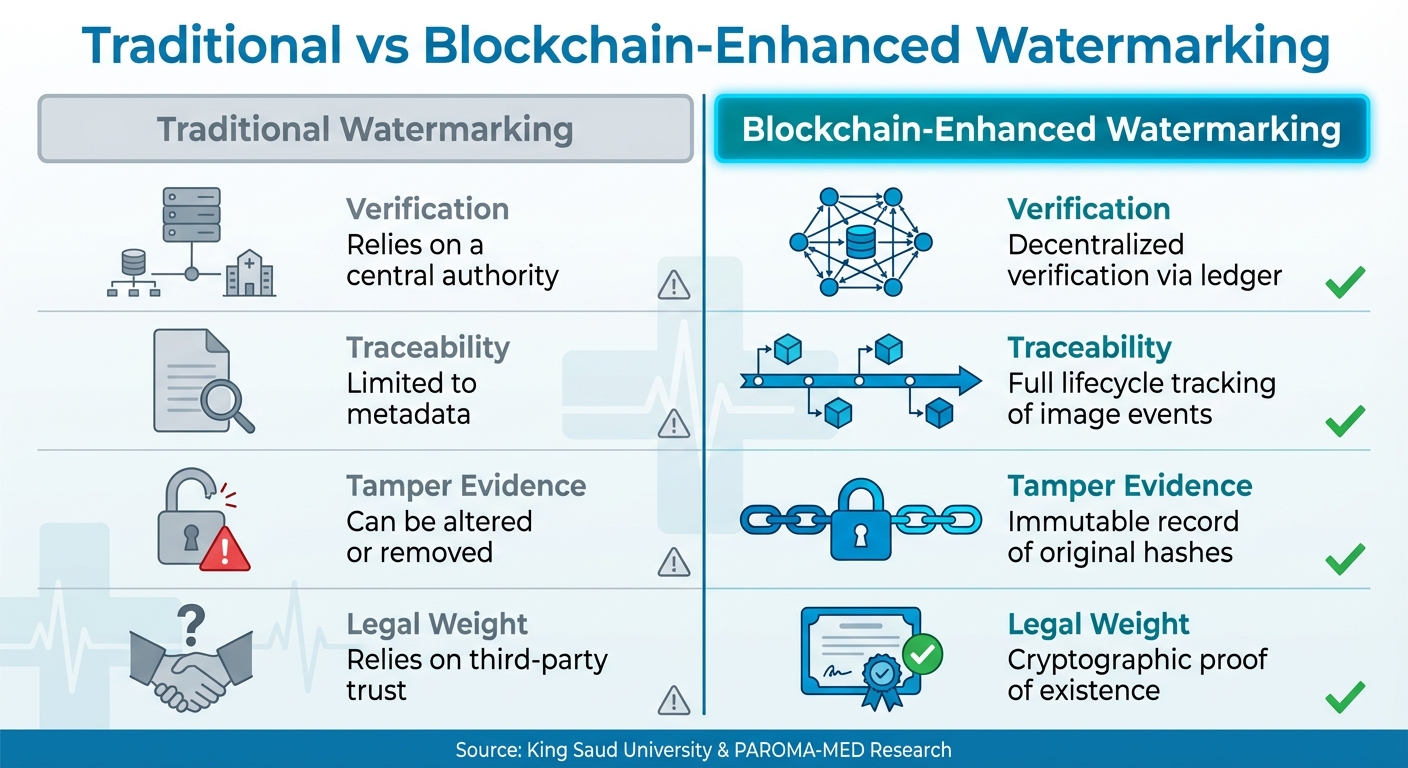
Traditional vs Blockchain-Enhanced Medical Image Watermarking Comparison
Blockchain technology, combined with advanced watermarking techniques, offers a powerful solution for protecting medical images. Here’s how it strengthens healthcare data security and efficiency.
Stronger Security and Data Integrity
By integrating frequency-domain watermarking techniques like DWT/DCT, AES encryption, and blockchain ledgers, this approach ensures robust, tamper-proof protection. Blockchain’s decentralized structure eliminates the risks of single points of failure, making it a reliable option for safeguarding sensitive medical data.
As researchers from King Saud University highlighted:
"The use of the blockchain is to accomplish authentication without the involvement of a trusted third party for the secrecy of the watermark so is not be exposed to anyone except the involved parties." [2]
Modern frameworks also ensure that the Region of Interest (ROI) within medical images remains 100% reversible. This means that even if parts of the image are modified, doctors can recover the original diagnostic data without any loss [8]. Additionally, these systems achieve impressive PSNR values of up to 68.75 dB, proving that high security doesn’t compromise image quality [5].
This level of security not only protects the data but also supports traceability and compliance with legal standards.
Better Traceability and Legal Evidence
Blockchain technology creates an immutable audit trail for every interaction with a medical image. From embedding to extraction and access, every event is recorded on a distributed ledger, ensuring a permanent and tamper-proof history [2][4].
For example, the PAROMA-MED project tracked 544,893 lung X-ray images used in training VGG-16 models for COVID-19 diagnosis. With cryptographic hashes stored on a private blockchain, the project ensured complete lifecycle tracking across multiple data centers [10].
For healthcare providers navigating regulations like HIPAA or GDPR, blockchain records provide undeniable proof of ownership and proper data management. In cases of disputes over unauthorized use of medical images, cryptographic proof via SHA-256 hashes can serve as irrefutable evidence [2][4].
| Feature | Traditional Watermarking | Blockchain-Enhanced Watermarking |
|---|---|---|
| Verification | Relies on a central authority | Decentralized verification via ledger [2] |
| Traceability | Limited to metadata | Full lifecycle tracking of image events [4] |
| Tamper Evidence | Can be altered or removed | Immutable record of original hashes [2] |
| Legal Weight | Relies on third-party trust | Cryptographic proof of existence [2] |
These features not only enhance security and accountability but also help streamline operations and reduce costs.
Lower Costs and Scalability
Blockchain-based watermarking reduces expenses by removing the need for intermediaries and centralized systems [2][6]. It’s also highly scalable. Lightweight CNN decoders, used for watermark extraction, require just 0.65 MB of storage, making real-time processing possible even on resource-limited medical devices [5]. This edge computing capability allows hospitals to authenticate images directly on IoMT devices, cutting down on bandwidth usage and latency.
The PAROMA-MED project demonstrated this scalability by processing over 544,893 medical images without affecting AI model performance [10]. Hybrid DWT-DCT frameworks have shown notable improvements, with a 28–35% boost in PSNR and a 12–15% increase in Normalized Correlation compared to older methods [5].
For healthcare organizations just starting with blockchain, platforms like ScoreDetect offer an easy entry point. Their Pro plan, priced at $11.31/month (billed annually), automates timestamping for PACS systems through Zapier integration. This allows providers to record cryptographic fingerprints without needing advanced blockchain expertise or significant IT resources.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Key Takeaways
Blockchain technology is redefining how medical images are verified and secured. By decentralizing image verification, it allows stakeholders to confirm the integrity and ownership of medical images with confidence. Every watermarking and access event is permanently recorded on the blockchain, establishing a reliable audit trail for legal and compliance purposes [2][4].
Cryptographic hashes play a crucial role in this process, identifying unauthorized changes instantly while maintaining diagnostic image quality. Metrics like a PSNR greater than 60 dB and SSIM values close to 1 highlight how these systems preserve the clarity and detail needed for clinical evaluations [1][5].
"The proposed medical image watermarking approach is the first method that demonstrates an effective solution to the medical image authentication problem using the blockchain, thus removing the need for trusted third parties." – King Saud University researchers [2]
Security measures like multi-layer frameworks have shown impressive results, such as PSNR values of 63.24 dB, ensuring that critical image regions remain reversible and diagnostically accurate [1]. These advancements create a solid foundation for future developments.
Future Developments in Blockchain and Watermarking
The next wave of innovation in blockchain and watermarking is poised to take medical image security to new heights. Lightweight CNN decoders, as small as 0.65 MB, are enabling real-time watermark extraction directly on Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices. This approach not only enhances security but also reduces bandwidth demands and latency by authenticating images locally [5].
Federated Learning is another promising development. The PAROMA-MED project, led by researchers like Reda Bellafqira from IMT Atlantique, has demonstrated how blockchain-watermarking frameworks can support decentralized AI training. By recording cryptographic hashes on a private blockchain, these systems ensure data security while maintaining the performance of AI models like VGG-16, which has been used for COVID-19 diagnosis [4].
Emerging concepts such as "imagechains" could revolutionize medical image storage. By treating images as blocks in a distributed ledger, these systems enable secure and seamless remote access across healthcare networks [3]. Additionally, zero-watermarking techniques, which verify image authenticity without altering pixel data, promise to maintain full diagnostic integrity while providing robust security [5][7].
Platforms like ScoreDetect are making these advanced technologies more accessible. Through automated workflows and integrations with tools like Zapier, they simplify the implementation of blockchain-based protection, bridging the gap between cutting-edge technology and practical application.
FAQs
How does blockchain enhance the security of watermarking in medical imaging?
Blockchain adds a robust layer of security to medical image watermarking by leveraging a tamper-resistant, decentralized ledger to maintain data integrity and accountability. This system ensures that watermarked images remain unaltered and that the watermark’s authenticity and ownership can be verified with confidence.
By storing a unique digital signature of the watermark securely, blockchain enables full traceability, making it easier to identify and address any misuse. This level of protection is crucial for safeguarding sensitive medical information and ensuring its proper handling.
How do cryptographic hashes ensure the security of medical images?
Cryptographic hashes play a key role in safeguarding the integrity of medical images by creating a unique digital fingerprint for each one. If an image is modified – whether by mistake or on purpose – the hash value will change, serving as an immediate alert to tampering or corruption.
In blockchain-based watermarking systems, hashes (or checksums) are used to confirm an image’s authenticity and integrity without needing to store the actual image data. This approach allows for quick detection of unauthorized changes while ensuring privacy and security – critical factors in healthcare settings.
How does blockchain ensure the authenticity and integrity of medical images?
Blockchain plays a crucial role in safeguarding medical images by creating a secure, time-stamped record of their existence. This is done through checksum generation, a process that produces a unique digital fingerprint for each image. Instead of storing the actual image, this fingerprint is saved on the blockchain, serving as an unchangeable proof that the image existed at a specific moment.
This approach not only secures sensitive medical data but also improves traceability. It ensures that any unauthorized changes or misuse of the images can be quickly identified. By using blockchain, healthcare providers can uphold trust and security when managing medical images.

