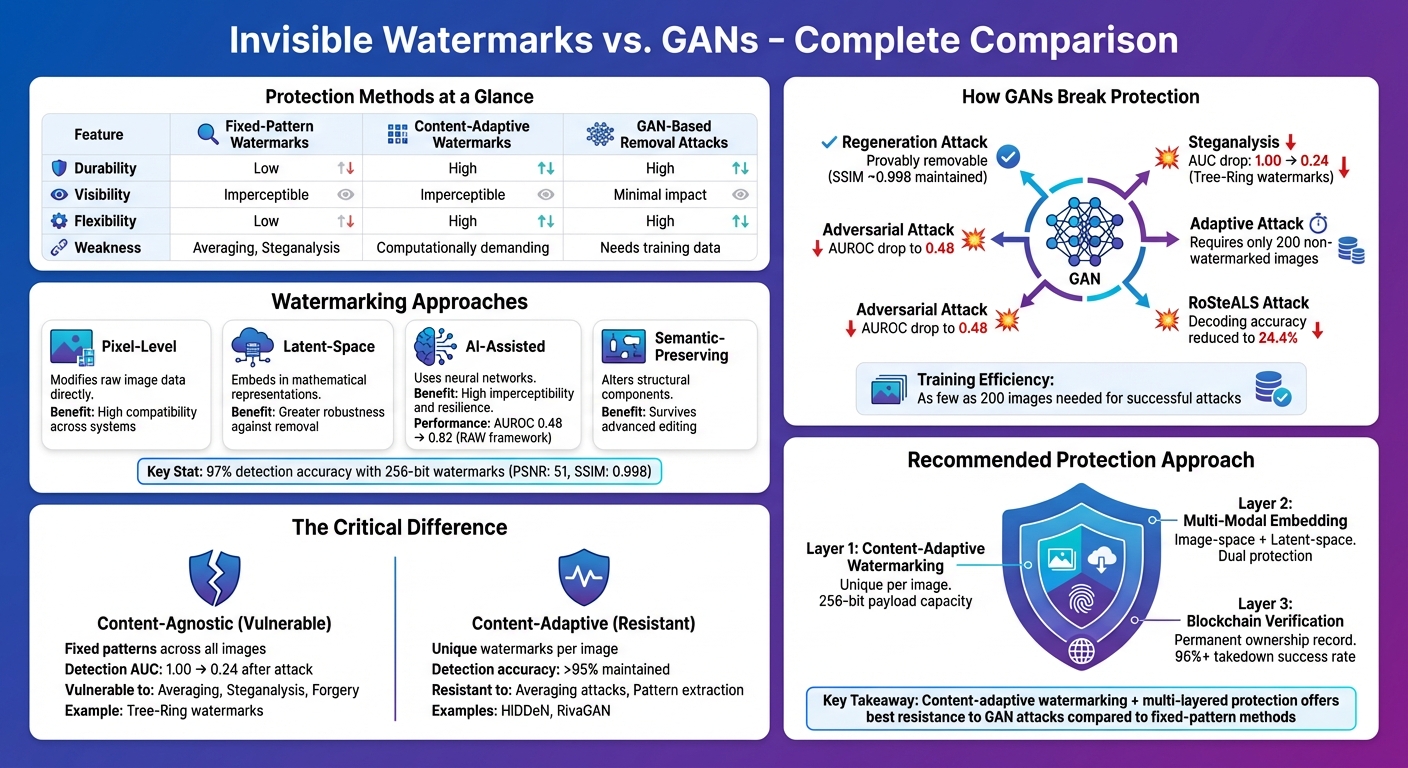
Invisible watermarks and GANs are locked in a technological battle. Invisible watermarks embed undetectable signals into digital content to prove ownership, while GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) are being used to remove these watermarks with alarming efficiency. Here’s the key takeaway: content-adaptive watermarking and multi-layered protection offer better resistance to GAN attacks compared to fixed-pattern methods.
Key Insights:
- Invisible Watermarks: Embed ownership data into images, videos, or text without altering the content’s appearance. Detection success rates can reach 97% even after transformations.
- GAN Attacks: Use AI to treat watermarks as noise and remove them while preserving image quality. Some attacks succeed with as few as 200 non-watermarked images.
- Weaknesses: Fixed-pattern watermarks are vulnerable to averaging and steganalysis. GANs exploit these weaknesses to erase or forge watermarks.
- Solutions: Content-adaptive watermarking, combining image and latent-space embedding, and blockchain verification provide stronger protection.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | Fixed-Pattern Watermarks | Content-Adaptive Watermarks | GAN-Based Removal Attacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | Low | High | High |
| Visibility | Imperceptible | Imperceptible | Minimal impact |
| Flexibility | Low | High | High |
| Weakness | Averaging, Steganalysis | Computationally demanding | Needs training data |
Businesses should adopt multi-layered strategies, including content-adaptive watermarking and blockchain verification, to protect digital assets from GAN-based threats. This approach ensures better resistance to attacks while maintaining ownership integrity.
Invisible Watermarks vs GAN Attacks: Comparison of Protection Methods and Vulnerabilities
Watermarking in Generative AI: Opportunities and Threats
How Invisible Watermarks Work
Invisible watermarks are a clever way to embed unnoticeable identifiers into digital content – like images, videos, audio, or even text – without disrupting the user experience. Using advanced neural networks, these watermarks embed signals that can later be retrieved to verify ownership. They work by altering either the visible pixels (image-space) or the internal data representations (latent-space) during content creation [3][4][5].
The latest techniques can encode 256-bit watermarks with impressive accuracy – achieving 97% detection success even after transformations. These methods ensure the content remains visually identical, with a peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) of 51 and a structural similarity index (SSIM) of 0.998 [3]. Moyang Guo highlights the effectiveness of this approach: "Watermark-based detectors consistently outperform passive detectors, both in the presence and absence of perturbations" [2]. Below, we explore the key techniques behind invisible watermarks.
Types of Invisible Watermarks
Several methods are used to embed invisible watermarks, each offering unique strengths:
- Pixel-Level Watermarks: These directly modify pixels or color channels in the image. While they work well across different systems, they can be more vulnerable to compression or blurring.
- Latent-Space Watermarks: Instead of altering the visible pixels, this method embeds data within the mathematical representations used by generative AI models. This approach can make watermarks more resilient to removal [4][5]. Combining latent-space and image-space techniques has been shown to improve resistance to attacks [4].
- AI-Assisted Watermarking: Leveraging neural networks and diffusion models (like SDXL-Turbo), these methods optimize the embedding process. For example, frameworks such as RAW have shown a significant boost in detection accuracy (AUROC) from 0.48 to 0.82 when dealing with adversarial attacks [5].
- Semantic-Preserving Watermarks: These adjust the structural elements of an image using generative priors. This makes them tougher to erase, even with advanced editing techniques like localized blurring or regeneration [8][11].
- Text-Based Watermarking: In AI-generated text, specific codes can be embedded in punctuation or word patterns. These identifiers are undetectable to readers but can be picked up by software [9].
| Watermarking Approach | Mechanism | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel-Level | Modifies raw image data/pixels directly | High compatibility across systems |
| Latent-Space | Embeds data in mathematical representations | Greater robustness against removal attempts |
| AI-Assisted | Uses neural networks to embed data | High imperceptibility and resilience |
| Semantic-Preserving | Alters structural components of the image | Survives advanced editing techniques |
| Text-Based | Embeds codes in punctuation or word patterns | Protects written content invisibly |
Each method offers a tailored solution for protecting digital assets while maintaining their original quality.
Business Benefits of Invisible Watermarks
Unlike passive detection methods – which rely on identifying artifacts after the content has been distributed – watermarking integrates identifiers directly into content during its creation. This makes it easier to track and verify ownership without needing external triggers or keys, as was common with older techniques [2][10]. If unauthorized use is discovered, the embedded watermark serves as concrete evidence, supporting legal actions or takedown requests.
"By combining high imperceptibility, extended payload capacity, and resilience to manipulations, InvisMark provides a robust foundation for ensuring media provenance" – Rui Xu, Lead Author [3]
Additionally, embedding complex data such as UUIDs (universally unique identifiers) allows businesses to track their assets across multiple distribution channels. Solutions like ScoreDetect take this further by integrating watermarking with automated tools for discovery, analysis, and takedown actions. These advanced capabilities are particularly crucial in combating GAN-based exploits, which will be discussed in the next sections.
How GANs Remove Watermarks
Attackers have found ways to exploit GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) to bypass watermark protections. By treating watermarks as noise, GANs can reconstruct digital content, removing these embedded signals while keeping the image’s meaning intact [12].
Watermarks that use a fixed pattern across images, known as content-agnostic watermarks, are particularly vulnerable. Attackers can average multiple samples to isolate and subtract the watermark pattern. This method doesn’t require knowledge of the original watermarking algorithm, making it a "blackbox" attack – effective even when the protection method is kept secret [1]. This highlights a significant weakness in traditional watermarking methods and sets the stage for understanding how GANs operate in these attacks.
The GAN Attack Process
The process of using GANs to remove watermarks typically involves two main steps. First, attackers introduce controlled noise to a watermarked image, effectively masking the embedded signal. Next, a generative model, like a GAN or diffusion model, reconstructs the image from this noisy version, maintaining high visual quality while erasing the watermark [12].
Some attacks go a step further with specialized remover networks. These networks use tools like GradCAM (Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) to create heatmaps that locate the watermark’s embedded information. Once identified, the remover network trains itself to reduce the accuracy of the watermark decoder while preserving the image’s quality. This dual optimization ensures the watermark is removed without compromising the image’s appearance [4].
"Content-agnostic watermarking techniques, including Tree-Ring, are vulnerable to steganalysis attacks, unmasking their hidden fragility." – Pei Yang et al. [1]
For watermarking systems like Tree-Ring, which rely on diffusion-based methods, attackers reverse-engineer latent noise to detect and remove patterns in the frequency domain [1]. Adaptive attacks can refine their methods using as few as 200 non-watermarked images, making the process both efficient and effective [6].
Breaking down these technical steps helps explain why GAN-based attacks are so successful.
GAN Attack Success Rates
The success of GAN-driven attacks varies depending on the type of watermark. For example, steganalysis-based methods can drastically reduce the detection Area Under the Curve (AUC) of Tree-Ring watermarks from a perfect 1.00 to just 0.24 [1]. Similarly, for the RoSteALS watermarking scheme, attacks reduced decoding accuracy to only 24.4% [1].
| Attack Method | Target Watermark Type | Effectiveness (Detection Metric) | Image Quality Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Regeneration | Pixel-level / Invisible | High (Provably removable) [12] | Minimal (SSIM ~0.998) [3] |
| Steganalysis | Content-Agnostic | High (AUC drop from 1.00 to 0.24) [1] | Very Low (artifacts disappear) [1] |
| Adversarial | Decoder-based | High (AUROC drop to 0.48) [5] | Minimal (imperceptible noise) [7] |
| Adaptive | Generator-embedded | High (requires only 200 images) [6] | Variable |
Content-agnostic watermarks face the greatest risks. In some cases, attackers have forged watermarks using extracted patterns, achieving 0% detection accuracy and completely bypassing authentication systems with just a 1% False Positive Rate [1]. On the other hand, content-adaptive watermarking methods like HiDDeN and RivaGAN have shown stronger resistance, maintaining detection accuracy above 95% even under steganalysis attacks [1].
These findings highlight the growing difficulty in protecting digital assets from advanced AI-based attacks.
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Invisible Watermarks vs. GANs: Direct Comparison
When you compare invisible watermarks with GAN-based attacks, the differences in embedding methods and vulnerabilities become clear. A watermark’s success depends heavily on how it’s integrated and the weaknesses it exposes. Here’s a breakdown of these differences in a straightforward table.
Comparison Table: Strength, Visibility, and Flexibility
The performance of watermarking approaches varies significantly based on their core characteristics. Content-agnostic methods rely on static patterns applied across all images, while content-adaptive techniques tailor the watermark to the unique features of each image.
| Feature | Content-Agnostic Watermarks | Content-Adaptive (GAN-based) | GAN-based Removal Attacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability | Low; prone to averaging | High; withstands distortions | High; removes pixel-level data |
| Visibility | Imperceptible (High PSNR) | Imperceptible (High PSNR) | Minimal quality impact |
| Flexibility | Low; fixed patterns | High; adapts to content | High; trains on specific watermarks |
| Primary Weakness | Vulnerable to steganalysis | Computationally demanding | Needs significant compute/data |
Content-adaptive methods like HiDDeN and RivaGAN show strong resistance to steganalysis attacks. In contrast, content-agnostic approaches such as Tree-Ring can see their detection performance plummet – from a perfect AUC of 1.00 to as low as 0.24 [1]. This stark difference underscores the importance of tailored strategies for watermarking. These distinctions also pave the way for understanding how GANs target and exploit watermark vulnerabilities.
Watermark Weaknesses and GAN Exploits
GANs take advantage of several key vulnerabilities in traditional watermarking systems:
- Fixed Pattern Vulnerability: Content-agnostic watermarks embed static patterns that attackers can extract by averaging multiple watermarked images. Once the pattern is isolated, it can be subtracted from new images – or even forged onto clean ones – without needing prior knowledge of the watermarking algorithm [1].
- Low-Level Propagation: Techniques like Tree-Ring introduce ripple patterns in the Fourier domain by modifying initial noise in diffusion models. These patterns, once detected, can be removed with minimal impact on image quality [1].
- Regeneration Exploits: GAN-based attackers can sidestep pixel-level watermarks entirely by regenerating the image’s content from scratch. This process destroys the mathematical relationships needed for decoding the watermark while maintaining an impressive visual quality, often achieving SSIM values around 0.998 [3].
- Localized Blurring Attacks: Using GradCAM heatmaps from watermark decoders, attackers can pinpoint the regions containing the watermark. By applying targeted blurring to these areas, they can erase the watermark while keeping the rest of the image intact [4].
"Watermarking is not robust against an adaptive white-box attacker who controls the generator’s parameters." – Nils Lukas, Researcher [6]
This evolving landscape highlights the challenges of securing watermarks against increasingly sophisticated GAN-based strategies.
Protection Strategies and Business Recommendations
Semantic-Preserving Watermarks for Better Defense
Switching from fixed-pattern watermarks to content-adaptive approaches has proven to be a stronger defense against GAN-based removal techniques. Unlike traditional methods that apply the same invisible watermark to all images, content-adaptive strategies tailor the watermark’s placement and intensity based on an image’s unique characteristics. This makes it much harder for attackers to pinpoint and remove a consistent pattern.
Content-adaptive watermarks are particularly effective because they eliminate the possibility of isolating a fixed pattern through averaging techniques. Since each watermark is uniquely structured, attackers can’t rely on standard methods to extract and erase it.
"Content-adaptive methods typically offer better robustness against image processing distortions, while content-agnostic methods are computationally lighter and easier to implement." – Pei Yang, Hai Ci, Yiren Song, and Mike Zheng Shou, National University of Singapore [1]
For businesses managing high-value intellectual property, using unique watermark keys per user or content set adds another layer of complexity for attackers. This approach not only prevents reverse-engineering of the watermarking algorithm but also retains high accuracy even after image manipulation. With this method, businesses can embed 256-bit payloads – enough for unique identifiers and error correction codes – without compromising the visual quality of the image [3].
By adopting these adaptive techniques, companies can bolster their defenses even further when combined with other protective measures.
Combining Multiple Protection Methods
No single method can guarantee complete security, which is why a layered defense strategy is crucial. The most robust solutions combine invisible watermarking with external verification tools like blockchain timestamping. This ensures that even if a GAN successfully removes the watermark, an unalterable record of ownership remains.
Platforms like ScoreDetect enhance watermarking by integrating blockchain-based copyright verification. This system generates a checksum of your content and timestamps it on the blockchain, creating a permanent proof of ownership. Even if an attacker regenerates the image and removes the embedded watermark, the blockchain timestamp provides irrefutable evidence of ownership.
For enterprises requiring advanced protection, multi-modal watermarking – embedding both image-space and latent-space watermarks into a single asset – offers a powerful solution. Research shows that GAN-based remover networks struggle to erase both layers without severely degrading the image quality [4]. When paired with ScoreDetect’s blockchain verification and takedown tools (boasting over 96% success rates), this approach provides a comprehensive shield against unauthorized usage.
"Watermark-based detectors consistently outperform passive detectors, both in the presence and absence of perturbations." – Moyang Guo et al. [2]
A multi-layered strategy creates multiple hurdles for attackers. Businesses should focus on content-adaptive watermarking for immediate detection, incorporate error correction codes to ensure payload integrity under distortion, and use blockchain timestamps to establish long-term ownership. This approach not only makes it harder for attackers to succeed but also allows for updates to individual layers as new threats surface.
Conclusion
Invisible watermarks face challenges when it comes to resisting GAN-based attacks. Fixed-pattern watermarks and diffusion methods often fall short, as they can be defeated through simple techniques like averaging or steganalysis [1][13].
While traditional watermarking methods struggle, content-adaptive, multi-modal protection offers a more reliable solution. Watermark-based detection systems consistently outperform passive methods, maintaining their accuracy even when images are altered. For instance, InvisMark achieves an impressive 97% bit accuracy under distortion (SSIM 0.998) [3], and RAW boosts detection performance from 0.48 to 0.82 AUROC [5].
To effectively counter these evolving threats, businesses need to adopt a layered defense strategy. This includes using content-adaptive watermarking to resist averaging attacks, embedding watermarks in both image and latent spaces for redundancy, and integrating blockchain verification to secure ownership. Combining these methods not only makes it harder for attackers to succeed but also strengthens long-term content protection.
Comprehensive platforms play a key role in this approach. For example, ScoreDetect combines invisible watermarking with blockchain verification. Even if a watermark is removed, the blockchain timestamp remains as irrefutable proof of ownership. By embedding a watermark and recording it on the blockchain, businesses gain dual protection: the watermark offers immediate proof, while the blockchain provides a permanent, tamper-proof record that can withstand advanced GAN-based removal techniques. With automated takedown systems achieving over 96% success rates, this multi-layered approach turns potential vulnerabilities into a solid defense.
As the arms race between protection technologies and AI attacks intensifies, adaptive and multi-modal systems are no longer optional – they’re essential. By leveraging content-adaptive watermarking, embedding techniques, and blockchain verification, businesses can stay ahead of attackers and ensure their content remains secure, no matter how sophisticated the threats become.
FAQs
What’s the difference between content-adaptive and fixed-pattern watermarks?
Content-adaptive watermarks adjust to the specific features of the content they’re embedded in, making them tougher to detect and tamper with. On the other hand, fixed-pattern watermarks rely on a static design that doesn’t change, regardless of the content. This fixed nature can make them easier to remove or distort.
Because they adapt to the content, content-adaptive watermarks are more resilient against advanced attacks, including those powered by AI, such as generative models or diffusion techniques. This adaptability offers a more secure way to safeguard digital assets and confirm ownership.
How do GANs effectively remove invisible watermarks?
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are incredibly skilled at eliminating invisible watermarks. Their strength lies in their ability to closely analyze and replicate visual content with a high level of precision. By leveraging advanced methods like generative autoencoders – such as variational autoencoders and diffusion models – GANs can detect and remove watermarks while preserving the original content’s quality and appearance.
These models are trained to recognize and reconstruct patterns, enabling them to erase embedded watermarks in a way that looks natural. This capability underscores their effectiveness in bypassing watermark protections and highlights the growing need for stronger, more advanced watermarking techniques.
What are the advantages of using watermarking with blockchain for content protection?
Combining invisible watermarking with blockchain verification offers a powerful way to safeguard digital assets. Invisible watermarking works by embedding hidden markers within content – like images or videos – to confirm ownership or authenticity. Blockchain complements this by storing these markers in a decentralized, tamper-resistant ledger, making it nearly impossible to alter the content’s origin or authenticity.
This combination doesn’t just help identify unauthorized use; it also creates a clear, traceable record of ownership and distribution. It streamlines legal processes by providing undeniable proof of ownership and can even automate takedown actions when violations occur. Together, these technologies enhance digital rights management, curb piracy, and provide lasting protection for your valuable content.

