AI audio watermarking is reshaping how audio content is protected, especially in low-bitrate formats like MP3 and AAC. By embedding digital signatures using deep learning, this technology ensures ownership verification and content integrity, even under heavy compression or editing. Unlike older methods, AI-driven techniques achieve far lower error rates, making them highly effective against piracy, deepfakes, and voice cloning threats.
Key Takeaways:
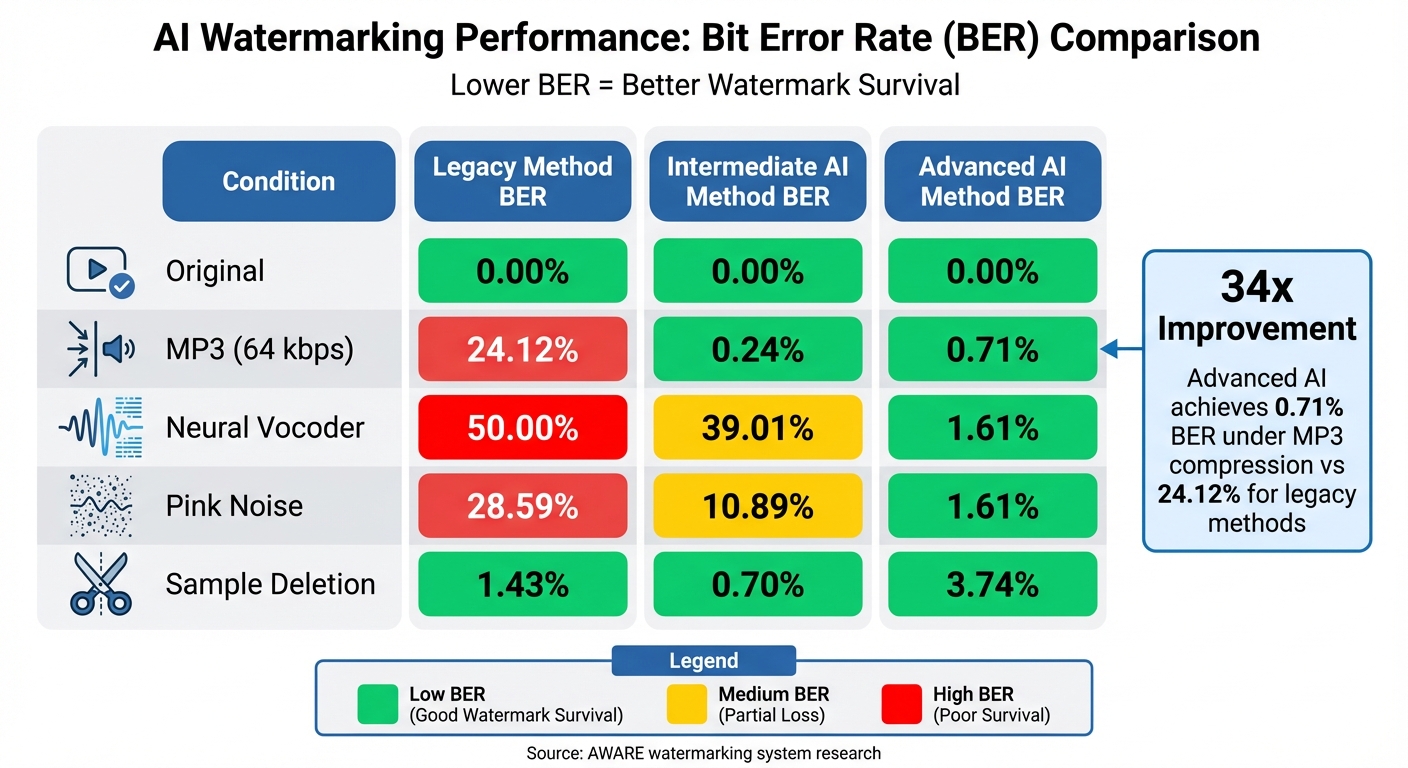
- Performance: AI watermarking systems like AWARE achieve a Bit Error Rate (BER) as low as 0.71% under 64 kbps MP3 compression, compared to 24.12% for older methods.
- Resilience: Neural networks, psychoacoustic models, and adversarial training ensure watermarks survive compression, cuts, and distortions.
- Applications: Media companies use these tools to protect music, films, and generative AI content, complying with regulations like the EU AI Act.
- Enterprise Solutions: Platforms like ScoreDetect combine watermarking with blockchain for tamper-proof copyright verification.
AI watermarking is becoming essential for safeguarding digital content in an era of increasing piracy and synthetic media.
Challenges in Low-Bitrate Audio Watermarking
Keeping Watermarks Inaudible
Low-bitrate audio files present a unique challenge: there’s so little space available that even slight changes can create noticeable distortions [2]. Traditional watermarking systems often fail here because they apply uniform modifications across the file. This approach doesn’t account for quieter sections, where even minor changes can be easily heard. AI-driven techniques like AWARE take a smarter approach, using level-proportional perceptual budgeting. This means louder sections get larger watermark changes, while quieter parts are modified more subtly [2].
Another standout innovation is SilentCipher, the first deep learning model to use psychoacoustic-based thresholding. This ensures any watermark changes stay below the threshold of human hearing [1]. Additionally, AWARE confines its modifications to the midband frequency range (500 Hz to 4,000 Hz) and avoids phase embedding, which helps maintain inaudibility even after low-pass or high-pass filtering [2]. These strategies are particularly important because heavy compression can amplify any audible artifacts.
Surviving Compression
Lossy compression formats like MP3 and AAC are notorious for eliminating audio data deemed unnecessary, which often includes subtle watermark signals. For instance, traditional systems like WavMark struggle significantly, with a Bit Error Rate (BER) of 24.12% under 64 kbps MP3 compression. In such cases, the watermark becomes unreadable [2].
"Neural compression techniques pose the most significant challenge, even when algorithms are trained with such compressions", says Yigitcan Özer, a researcher focused on watermark resilience [6].
Neural codecs are an even bigger hurdle. Under neural vocoder resynthesis, AudioSeal records a BER of 39.01%, while WavMark completely fails at a BER of 50% [2]. To combat this, AI-based systems incorporate pseudo-differentiable compression layers during training. These layers simulate codec distortions, teaching the network how to withstand them [1]. AWARE goes a step further with its Bitwise Readout Head (BRH), which gathers evidence across the entire audio file. This approach allows it to reliably detect watermarks even when large portions of the file are compressed or removed, achieving an impressive BER of just 0.71% under 64 kbps MP3 compression [2].
Data Capacity Limits
Low-bitrate files also restrict how much data can be embedded in the audio. There’s a tradeoff here: stronger watermarks are more resilient but carry less data, while higher-capacity watermarks are more prone to tampering [7].
"Stronger, more robust watermarks are often less capable of carrying a large amount of data, while watermarks with more capacity may be more susceptible to manipulation", explains Resemble AI [7].
The low entropy of these files further limits capacity, and pushing these limits can result in audible artifacts [8]. Some enterprise applications also require a minimum audio duration – often around two minutes – to reliably extract the watermark [9]. AI-driven adversarial optimization offers a solution here, identifying the best frequency bins to maximize capacity without compromising inaudibility. By simulating potential attacks during the embedding process, these systems determine where data can be densely hidden while remaining undetectable. Techniques like AWARE also use time-order–agnostic detection, which combines weak signals across the entire file. This ensures accurate decoding even if sections are cut or heavily compressed [2].
The move from traditional watermarking methods to AI-powered adversarial techniques has been a game-changer, addressing the balance between robustness and capacity under intense compression conditions.
sbb-itb-738ac1e
AI Music Copyright: The Watermarking Solution Explained
AI Techniques for Watermark Embedding
AI Audio Watermarking Performance: Bit Error Rates Across Compression Methods
Patchwork Algorithm with AI Enhancements
AI advancements are tackling the dual challenges of making watermarks both inaudible and resilient under low-bitrate compression. Traditional patchwork watermarking relies on fixed, pseudo-random adjustments at the sample level. The AI-enhanced approach, however, uses adversarial optimization to fine-tune frequency adjustments. This technique identifies the smallest frequency changes that maximize detection while keeping the watermark imperceptible to human ears [2]. Essentially, the algorithm learns which frequency ranges can handle more significant modifications without becoming noticeable.
Building on level-proportional perceptual budgeting, AI further refines these adjustments across varied audio segments. Models are trained using "audio attack pipelines" – simulations of noise, compression, and filtering – to prepare the watermark for neural codecs like Encodec and Descript Audio Codec. These codecs often strip out traditional watermarks that aren’t robust enough [10].
"Watermarking algorithms and neural codecs compete for the same space… neural codecs will end up removing imperceptible watermarks", explains Sony AI [10].
By employing time-frequency adversarial techniques, these algorithms can distribute watermark bits strategically, ensuring they survive challenges like temporal cuts, splicing, and desynchronization [2]. This optimization, combined with neural networks, strengthens spectrogram processing for even greater resilience.
Neural Networks for Spectrogram Processing
Neural networks complement frequency adjustments by improving watermark detection through advanced spectrogram analysis. Instead of raw spectrograms, these networks now focus on Mel-spectrograms, which group spectral energy into perceptually relevant bands. This approach significantly reduces time-frequency distortions. For example, one study found that using a Mel-based detector dropped the Bit Error Rate (BER) from 50.30% to a mere 1.61% when processed through a neural vocoder [2].
Modern detectors employ 1D convolutions with a kernel size of 1, enabling them to process time frames independently and avoid "temporal mixing." This design ensures that watermarks remain detectable even when the audio is cut or reordered. A kernel size of 1 achieves a BER of 5.53% under time-stretching, compared to 13.96% for larger kernels [2].
A key feature in these models is the Bitwise Readout Head (BRH). This component uses paired convolutional filters to gather temporal evidence across the spectrogram, producing a single score per watermark bit. The BRH is position-agnostic, meaning the watermark remains detectable even if the audio’s length or position changes. For instance, BRH-based models maintain a low 3.74% BER under sample deletion, whereas models with fully connected layers can see BERs spike to 30.91% [2].
"The detector directly predicts for each time step (1/16k of a second) if the watermark is present or not, which makes it ultra fast and suitable for real-time applications", says Pierre Fernandez, a researcher at Meta AI [4].
These neural network-based detectors are not only more accurate but also incredibly fast – up to 1,000 times faster than prior methods [4]. They achieve this speed by using "push loss" objectives, which ensure the detector confidently identifies watermark bits (±1) even when the signal is partially degraded [2].
Error Correction and Frequency Modulation
Modern AI models integrate compression-aware training to build robustness directly into the watermarking process, outperforming traditional post-hoc error correction methods [1][3].
Systems like AWARE embed watermarks within specific frequency bands (500 Hz to 4,000 Hz) of the STFT magnitude, avoiding phase-domain embedding, which is more vulnerable to low-bitrate compression. This approach has achieved a BER of just 0.71% under MP3 compression at 64 kbps, compared to 24.12% for older methods [2].
"Watermark detection differs fundamentally from object/keyword detection… It is a weak, distributed pattern, encoding bits that must be sequence-consistent under time-warping and cutting", explains Kosta Pavlović, lead researcher [2].
The Bitwise Readout Head further strengthens resilience by aggregating temporal evidence across the audio file. This design ensures that even with aggressive compression or large signal cuts, the watermark can still be reconstructed. For example, under pink noise corruption, AI-driven watermarking maintains a BER as low as 1.61%, while baseline models see errors soar past 28% [2].
| Condition | Legacy Method BER (%) | Intermediate AI Method BER (%) | Advanced AI Method BER (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| MP3 (64 kbps) | 24.12 | 0.24 | 0.71 |
| Neural Vocoder | 50.00 | 39.01 | 1.61 |
| Pink Noise | 28.59 | 10.89 | 1.61 |
| Sample Deletion | 1.43 | 0.70 | 3.74 |
This focus on "robustness by design" has shifted the paradigm. Instead of relying solely on error correction, architectures are now built to withstand temporal edits and desynchronization from the ground up [2].
Applications and Enterprise Integration
Use Cases in Media and Entertainment
Music labels and film studios face constant challenges in protecting their intellectual property. AI audio watermarking offers a solution by embedding invisible identifiers into audio files. These identifiers remain intact through compression, streaming, and even re-recording, making it possible to secure copyrights, trace content origins, and detect deepfakes [5].
In September 2024, researchers from Meta (FAIR), Inria, and Hebrew University showcased a latent watermarking method using the MusicGen model. This approach involved training a 1.5 billion-parameter model on 20,000 hours of licensed, pre-watermarked music. The results were impressive, with the watermark achieving an Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) of 0.999. Even when alternative decoders like Multi-Band Diffusion or HiFi-GAN were used, the watermark remained detectable [5].
By embedding watermarks directly into the latent representation during model training, companies can ensure that every generated output is inherently protected. This method addresses a key weakness of post-generation watermarking, which can often be bypassed by altering processing code. The system achieves a True Positive Rate above 0.95, with a False Positive Rate as low as 0.0001 [5].
"Watermarking can help trace content origin and support regulatory efforts. It is not a standalone solution and should be complemented with measures like policies, education, or monitoring."
– Robin San Roman, Pierre Fernandez, Antoine Deleforge, Yossi Adi, and Romain Serizel [5]
Beyond music, AI audio watermarking plays a role in preventing misuse like voice cloning and supports transparency in AI-generated content. Regulatory frameworks, such as the EU AI Act, increasingly highlight watermarking as a critical tool for labeling synthetic content and maintaining traceability [2]. Modern detection systems can even identify ownership in snippets as short as 1/16,000th of a second, making them highly effective at spotting pirated clips on social media and streaming platforms [4].
These advancements not only safeguard creators but also provide robust solutions for enterprise-level security.
ScoreDetect for Enterprise Solutions
Building on these advancements, ScoreDetect offers a comprehensive enterprise solution for audio protection. This platform combines invisible watermarking, automated discovery, and quick takedown capabilities to safeguard low-bitrate audio files. By embedding watermarks in the time–frequency domain using adversarial techniques, the system ensures they remain inaudible while maintaining high speech intelligibility (PESQ/STOI scores). Its Bitwise Readout Head (BRH) architecture enhances reliability, enabling accurate watermark decoding even when audio has been altered through cutting, splicing, or desynchronization [2].
ScoreDetect delivers impressive performance metrics: a low Bit Error Rate (BER) of 0.71% under 64 kbps MP3 compression, 1.61% under pink noise corruption, and 1.43% even with 8-bit linear PCM quantization [2].
The platform’s core capabilities include:
- Prevent: Invisible watermarking to deter unauthorized use.
- Discover: Intelligent web scraping with a 95% success rate in bypassing prevention measures.
- Analyze: Quantitative content matching to provide proof of unauthorized use.
- Take Down: Automated delisting notices with a 96% success rate.
ScoreDetect integrates seamlessly with over 6,000 web apps via Zapier, making it easy to incorporate into existing enterprise workflows.
For organizations seeking even more advanced protection, InCyan, the company behind ScoreDetect, offers Tectus. This solution provides blind watermarking for images, videos, and audio, delivering invisible proof of ownership that accelerates copyright enforcement without compromising user experience.
Additionally, the platform extends its protection with blockchain-based copyright verification.
Copyright Protection with Blockchain
ScoreDetect leverages blockchain technology to create tamper-proof proof of ownership without storing the actual audio files. Instead, it records a SHA256 checksum of the watermarked content on a public blockchain. This creates a secure and verifiable record of ownership without the need to store large audio assets. By matching an audio file’s hash to the one recorded on the blockchain, organizations can demonstrate ownership tied to a specific date and time [2].
This blockchain integration aligns with global policy frameworks like the EU AI Act (Regulation 2024/1689), which emphasize content traceability and provenance [2]. The system ensures a defensible chain of custody from creation to distribution, making it a strong asset in legal disputes.
ScoreDetect’s WordPress plugin automates this process by recording a SHA256 checksum for every published or updated article. This not only strengthens copyright protection but also enhances SEO by signaling content authenticity – a key factor in Google’s E-E-A-T framework.
Conclusion
AI-driven audio watermarking has reshaped how businesses protect low-bitrate audio files. Unlike traditional methods that falter under compression, AI techniques remain effective even with MP3 compression at 64 kbps, achieving a bit error rate (BER) as low as 0.71%. By leveraging psychoacoustic models, these watermarks stay hidden to the human ear, even after being subjected to cuts, splices, or neural codec processing [1][2].
This approach embeds tracking data during the creation process, eliminating the need to identify tampered files after the fact. As generative AI continues to advance in quality, this proactive strategy is becoming increasingly critical.
Enterprise solutions have embraced these advancements. For instance, ScoreDetect offers a robust suite of tools, including invisible watermarking, automated discovery with a 95% success rate, and takedown notices that are over 96% effective. Its blockchain integration ensures tamper-proof ownership records without requiring the storage of actual audio files, aligning with new regulations while reinforcing copyright protections.
For companies managing streaming content or distributing generative models, precise detection is now a must. Modern systems can identify watermarks at intervals as short as 1/16,000th of a second – making them up to 1,000 times faster than earlier methods. This level of speed and precision provides real-time, scalable protection for enterprises [4].
With its ability to withstand unauthorized use, counter deepfakes, and combat piracy, AI-powered audio watermarking has become a cornerstone for safeguarding digital content in today’s landscape.
FAQs
How does AI audio watermarking protect low-bitrate files from piracy?
AI audio watermarking protects low-bitrate audio files by embedding hidden and durable watermarks directly into the sound. These watermarks stay intact even after compression, editing, or other typical modifications, allowing the content to be reliably identified and authenticated.
This method adds a strong, traceable layer of security, making it easier to detect and combat piracy effectively.
How does AI-driven watermarking stay effective even after audio compression?
AI-powered watermarking stands out against audio compression thanks to its use of advanced techniques like adversarial optimization and perceptual modeling. These approaches allow watermarks to be embedded in a way that seamlessly integrates with the audio while staying strong against the typical changes caused by compression.
What sets AI-driven methods apart is their ability to handle a variety of distortions by using dynamic strategies such as localized embedding and robust optimization. This means the watermark can survive even in low-bitrate audio files while maintaining the original audio quality.
How does blockchain improve copyright protection in AI audio watermarking?
Blockchain technology enhances copyright protection in AI audio watermarking by creating a secure, tamper-resistant record of ownership. Instead of storing the actual audio file, it generates a unique checksum for the watermarked content. This checksum acts as verifiable proof of ownership, ensuring that details remain unchangeable and transparent. As a result, altering or removing the watermark without detection becomes nearly impossible.
Its decentralized design also streamlines the management of digital rights. Blockchain enables automated processes like content registration, verification, and takedown requests, while maintaining a clear, auditable ownership trail. This approach helps tackle digital piracy and prevents unauthorized sharing of AI-generated audio files.

