Audio watermarking is a method to protect digital audio from piracy and fraud by embedding undetectable signals into files. With the rise of AI-generated audio, securing content has never been more important. This guide explores how AI-based techniques outperform older methods, balancing audio quality with resilience against distortions like compression or tampering. Key takeaways include:
- AI Techniques: Advanced models (e.g., VAEs, GANs) ensure watermarks survive complex attacks.
- Optimization: Balancing imperceptibility with durability is critical to success.
- Applications: From protecting music to verifying AI-generated content, watermarking is widely used.
- Challenges: Neural compression and physical attacks can weaken watermarks, but newer methods are improving resistance.
- Tools: Platforms like ScoreDetect simplify embedding, detection, and enforcement.
For anyone managing audio assets, adopting AI-powered watermarking ensures better protection and authenticity in an era of evolving threats.
Audio Watermarking using Optimized DWT-SVD
Core Methods for AI-Based Watermark Embedding
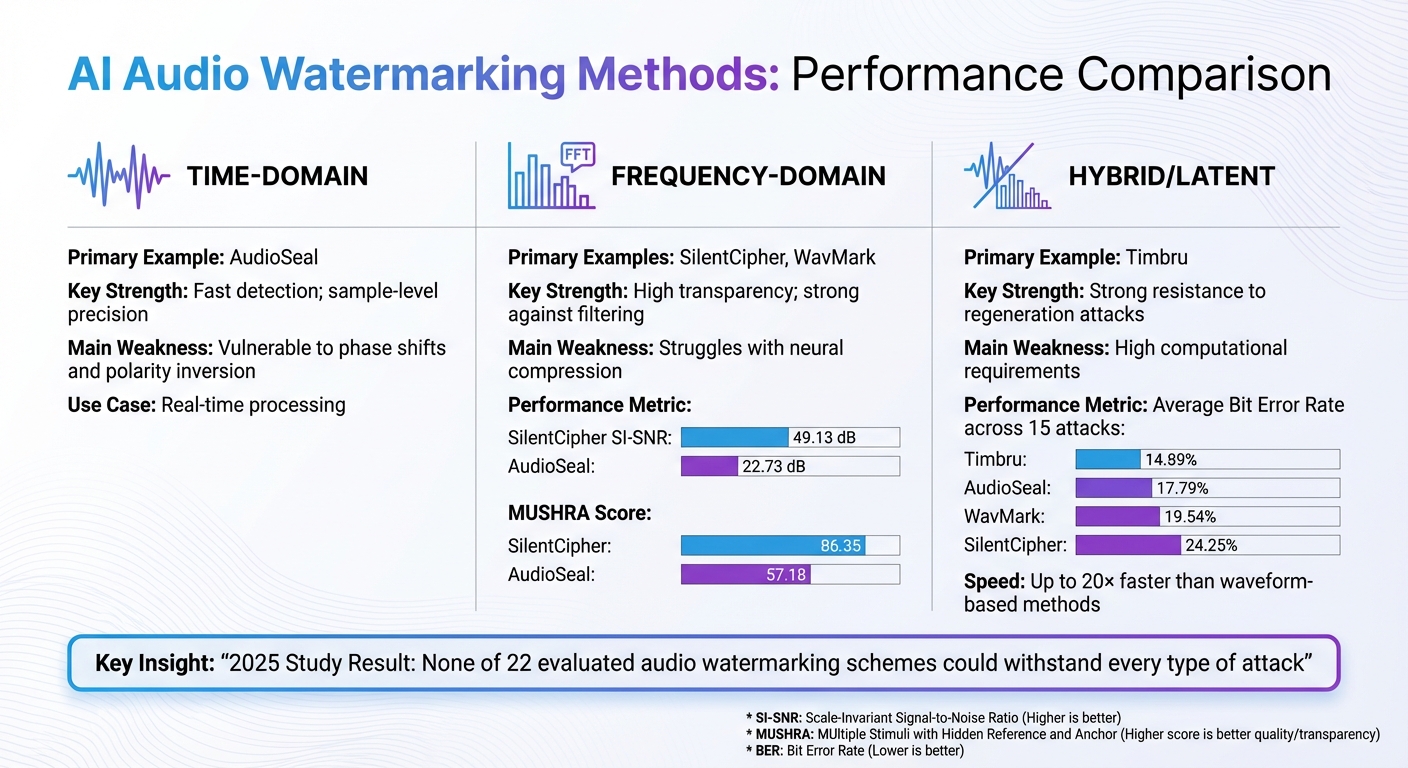
AI Audio Watermarking Methods Comparison: Time-Domain vs Frequency-Domain vs Hybrid Techniques
AI-powered audio watermarking revolves around three main approaches: time-domain, frequency-domain, and hybrid techniques. Each method balances key factors like invisibility, durability, and efficiency, forming the backbone of effective digital content protection. Let’s dive into these methods and their trade-offs.
Time-Domain Techniques
Time-domain methods embed watermarks by tweaking amplitude or timing at the sample level. This approach is great for pinpointing tampered sections, even in lengthy recordings.
These methods are simple, fast, and require less computational power. They also handle cropping or sample suppression attacks quite well [2]. However, they have limitations, such as being vulnerable to phase shifts and polarity inversions [5]. Traditional methods like Least Significant Bit (LSB) embedding often fall short when it comes to surviving standard audio transformations [4].
Frequency-Domain Techniques
Frequency-domain methods work by transforming the audio signal using techniques like FFT, DWT, or STFT, and embedding watermarks into specific frequency coefficients [4]. Tools like WavMark and SilentCipher operate in this domain. SilentCipher, for instance, delivers exceptional transparency, achieving a SI-SNR of 49.13 dB compared to AudioSeal‘s 22.73 dB [5]. However, neural compression can significantly reduce the accuracy of these methods [5].
"Watermarking algorithms and neural codecs compete for the same space… neural codecs will end up removing imperceptible watermarks." – Yigitcan Ozer, Researcher, Sony AI [5]
Hybrid Techniques for Better Performance
Hybrid methods combine the strengths of time-domain and frequency-domain techniques to deliver better performance in practical applications. These approaches embed watermarks in transformed signals while ensuring the changes maintain both time-specific and frequency-specific qualities [4].
Advanced AI models like Timbru operate in the latent space of pretrained models (e.g., VAEs) and use gradient optimization to improve resilience against attacks [2]. Timbru has shown impressive results, with an average bit error rate of 14.89% across various attack scenarios, outperforming alternatives like AudioSeal (17.79%) and WavMark (19.54%) [2]. Another hybrid technique, Timbre Watermarking, embeds marks into the amplitude of a spectrogram while preserving phase information, striking a balance between robustness and temporal accuracy [6].
| Method Category | Primary Example | Key Strength | Main Weakness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time-Domain | AudioSeal | Fast detection; sample-level precision | Vulnerable to phase shifts and polarity inversion |
| Frequency-Domain | SilentCipher, WavMark | High transparency; strong against filtering | Struggles with neural compression |
| Hybrid/Latent | Timbru | Strong resistance to regeneration attacks | High computational requirements |
While these advances are impressive, no method is foolproof. A 2025 study evaluating 22 audio watermarking schemes highlighted that none could withstand every type of attack, especially those involving physical distortions or AI-driven manipulations [4]. Ultimately, the choice of technique depends on specific needs – whether it’s real-time processing, seamless transparency, or enhanced resilience against complex removal attempts. These methods lay the groundwork for further optimization, which will be explored in the next section.
Key Considerations for Optimization
Optimizing audio watermarks is all about finding the right balance between keeping them undetectable to listeners and ensuring they remain intact under various conditions.
Balancing Imperceptibility and Durability
At the heart of audio watermarking lies a tricky balancing act. Modern systems tackle this by using two loss functions during optimization: one focuses on preserving the watermark against attacks (message loss), while the other ensures it stays inaudible (perceptual loss) [2]. But as you increase the bit payload, the robustness of the watermark can weaken, forcing a trade-off between capacity, imperceptibility, and durability [2][5].
"The trade-off between watermark imperceptibility and robustness against attacks remains at the center of audio watermarking." – Timbru Research Team [2]
One way to address this is by setting a Signal-to-Distortion Ratio (SDR) lower bound during the embedding process. This ensures the watermark doesn’t cross audible thresholds. For instance, SilentCipher uses SDR bounding to maintain imperceptibility, though this can sometimes result in lower bit recovery rates when faced with heavy compression [2][5]. In human evaluation tests, SilentCipher scored 86.35 on perceptual quality compared to AudioSeal’s 57.18 in MUSHRA testing [2]. Instead of applying a one-size-fits-all approach, per-audio gradient optimization adjusts the watermarking process for each specific audio file, achieving a better balance [2].
These strategies naturally lead to the use of psychoacoustic and adaptive techniques, which further refine how watermarks are embedded.
Using Psychoacoustic Models
Psychoacoustic models take advantage of how the human ear perceives sound, embedding watermarks in frequency bands where they’re masked by louder signals, making them nearly impossible to detect while maintaining robustness. This means quieter watermarks can "hide" in louder carrier signals within specific frequency or time ranges [3][4].
In June 2025, researchers from Tsinghua University and Tencent AI Lab introduced WAKE, a framework that used multi-scale Mel-spectrogram loss [3]. They found that without proper constraints, watermarks could cause noticeable "bursting" sounds at the edges of audio due to high-frequency energy stacking. By applying specific weighting to these edges, they eliminated these artifacts [3].
Instead of manually tweaking frequency coefficients, many modern systems rely on perceptual loss functions during training. This allows AI models to automatically pinpoint the best embedding regions [2][4]. It’s also crucial to test against advanced neural codecs like EnCodec or DAC, which are specifically designed to strip out imperceptible details [5].
Adaptive Techniques for Embedding
Adaptive embedding methods take things a step further by tailoring the process to the unique characteristics of each audio file. Unlike static strategies, which might struggle with diverse audio content, adaptive techniques dynamically adjust the watermark’s strength based on local audio traits. For example, louder sections can mask modifications more effectively, making them ideal for embedding [4].
One advanced method involves per-audio gradient optimization in latent space. Systems like Timbru use this approach by introducing perturbations to the latent representation of a pretrained Variational Autoencoder (VAE) [2]. This technique achieved an average bit error rate of 14.89% across 15 different attack types in 16-bit watermarking tests, outperforming both AudioSeal (17.79%) and SilentCipher (24.25%) [2]. Additionally, watermarking in latent space can be up to 20× faster than traditional waveform-based methods [1].
Localized watermarking, which adjusts embedding at the sample level, further enhances resilience, especially for segmented or streaming content [1][2][5]. This ensures watermarks remain detectable even in short clips or after significant cropping. Adding a "random attack" stage during embedding forces the system to create watermarks that can withstand real-time distortions like compression, noise, and filtering [2][5].
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Applications and Challenges
Applications in Content Protection
AI audio watermarking is a powerful tool for protecting intellectual property across various industries. In the music world, these systems embed invisible markers into audio tracks, which remain intact even after sharing, compressing, or modifying the files. This allows artists to track their work as it spreads across streaming platforms and social media channels [4][5]. Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Threads have adopted invisible watermarking to label AI-generated content automatically. This step gained prominence during the 2023 surge of fake AI-generated songs that imitated popular artists [1][4]. Beyond social media, watermarking plays a vital role in fraud prevention by verifying the authenticity of audio content. It’s also used by organizations to embed markers in training datasets, enabling them to confirm whether proprietary data was utilized in training third-party AI models [1].
Despite its many uses, watermarking faces notable challenges in real-world applications.
Common Challenges in Watermarking
Even with advancements, current watermarking systems struggle to survive all types of real-world distortions. A study examining 22 audio watermarking methods revealed that none were robust enough to withstand every tested attack [4]. One major hurdle comes from neural compression techniques like EnCodec and Descript Audio Codec, which often reduce bitwise accuracy to nearly zero [5].
"Watermarking algorithms and neural codecs compete for the same space… if we consider the limit situation where both algorithms successfully achieve their purpose, we believe that neural codecs will end up removing imperceptible watermarks." – Yigitcan Ozer et al., Sony AI [5]
Physical-level attacks, such as the "analog hole", also pose significant risks. This occurs when audio is played through speakers and re-recorded, with environmental noise and room acoustics distorting the signal enough to erase most watermarks [4]. AI-driven distortions, like voice conversion or text-to-speech techniques, can regenerate audio while stripping away the original watermark. Another challenge arises from watermark overwriting during multi-stage distribution. For example, models like AudioSeal and WavMark experience Bit Error Rates of 46% to 48% for the first watermark when a second is added, making it nearly impossible to trace the content back to its origin [3].
However, advanced solutions are being developed to address these issues.
ScoreDetect‘s Role in Advanced Optimization

To tackle these challenges, ScoreDetect has introduced cutting-edge techniques to enhance watermark resilience and detection. Through its Enterprise plan, ScoreDetect employs invisible, non-intrusive watermarking combined with automated detection and enforcement. These watermarks are designed to remain undetectable while resisting compression and format conversion. ScoreDetect’s targeted web scraping achieves a 95% success rate in bypassing prevention measures, quickly identifying unauthorized uses of watermarked content. Once detected, its analysis tools provide concrete evidence of misuse, enabling effective enforcement actions.
ScoreDetect also integrates blockchain technology to capture a checksum of the content without storing the actual digital asset. This creates verifiable proof of ownership and origin. Additionally, its automated takedown system boasts a success rate of over 96%, offering a comprehensive solution that addresses both the technical challenges of watermarking and the practical needs of large-scale content protection.
Best Practices for Implementation
Designing Watermarking Pipelines
When setting up your watermarking pipeline, consider a three-stage design: a transformation stage, an embedding module, and a verification system. For the transformation stage, techniques like STFT (Short-Time Fourier Transform) or VAE (Variational Autoencoder) latent spaces can prepare the audio for watermark embedding. The embedding itself can be powered by Invertible Neural Networks or gradient optimization techniques, while pretrained models like CLAP can handle verification tasks [2][3].
To make your watermark resilient, introduce a "random attack" simulation during training. This step mimics real-world distortions like compression or noise interference. Skipping this step might result in watermarks that work in controlled environments but fail when the audio is shared on platforms like social media or streaming services [2][5]. For high-value audio content, post-hoc gradient optimization offers a robust solution, though it may require up to an hour per stereo snippet [2].
Access control is another key component. Use key-controlled mechanisms to ensure only authorized users can extract the watermark. This approach also supports embedding multiple watermarks that coexist without overwriting each other. Frameworks like WAKE exemplify this by allowing layered protection that endures through multiple distribution stages [3]. To balance detection accuracy and audio quality, utilize multi-scale Mel Spectrogram analysis, which minimizes perceptual loss while maintaining the watermark’s invisibility [2][3].
These foundational choices prepare your pipeline for evolving challenges, ensuring durability as new distortions and threats emerge.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustment
Even with a well-designed pipeline, continuous monitoring is essential to maintain watermark effectiveness. The battle between watermarking algorithms and compression technologies is ongoing. As Sony AI researchers observed:
"Watermarking algorithms and neural codecs compete for the same space… neural codecs will end up removing imperceptible watermarks" [5].
This underscores a critical point: once a watermark is deployed, it cannot be "patched." Rigorous testing against emerging threats is necessary before release.
Your system should be tested against a wide range of distortions, from neural compression to advanced AI-driven attacks. These include techniques like voice conversion and text-to-speech regeneration, which can effectively strip watermarks by reconstructing the audio signal [4]. Adjust detection thresholds to reduce false positives while accounting for these evolving threats.
A study analyzing 22 audio watermarking schemes revealed that none could withstand all tested distortions. This highlights the importance of ongoing refinement to stay ahead of new attack methods [4].
Using Tools like ScoreDetect
Platforms like ScoreDetect simplify the watermarking process by combining key features: invisible embedding, automated detection, and blockchain-based ownership verification. This tool integrates seamlessly into the pipeline, offering end-to-end protection.
One standout feature is its web scraping capability, which achieves a 95% success rate in bypassing preventive measures to identify unauthorized use. Additionally, its automated takedown system handles enforcement efficiently, boasting a 96% success rate. This automation addresses both technical challenges, like watermark durability, and practical concerns, such as large-scale content protection. With ScoreDetect, you can focus on creating while leaving the heavy lifting of monitoring and enforcement to the platform.
Conclusion
Optimizing AI-driven audio watermarking requires a careful balance between being undetectable, maintaining durability, and ensuring adequate capacity. As the University of Hawaii at Manoa highlights, "None of the surveyed watermarking schemes is robust enough to withstand all tested distortions in practice" [4]. This underscores the need for ongoing refinement and the development of advanced tools to safeguard digital content effectively.
Emerging techniques like latent space optimization and post-hoc watermarking are proving far more effective than older methods such as LSB embedding or echo hiding. For instance, modern gradient optimization methods have demonstrated average bit error rates of around 14.89% across more than 15 types of attacks [2], showing a clear advancement over traditional approaches.
But the challenges aren’t just technical. Take the alarming case of scammers using an AI-generated CEO voice to authorize a fraudulent $243,000 transfer [4]. This incident highlights watermarking’s broader significance – it’s not just about protecting intellectual property. Watermarking plays a vital role in verifying authenticity, combating deepfakes, and maintaining trust in digital audio.
Addressing these challenges requires robust infrastructure. Tools like ScoreDetect offer an all-encompassing solution with invisible watermarking, automated monitoring, and enforcement capabilities. This comprehensive approach tackles both the technical complexity of making watermarks durable and the practical demands of protecting large-scale digital content.
The future of watermarking lies in rigorous testing across different domains, frequent updates, and adaptable tools. By sticking to these principles, we can build resilient watermarking systems for music, podcasts, voice recordings, and beyond.
FAQs
How does AI improve the durability of audio watermarks against advanced attacks?
AI-powered audio watermarking takes protection to the next level by embedding watermarks that can endure even the toughest distortions. Using cutting-edge approaches like deep learning, these systems are trained to handle a wide range of challenges – compression, noise, reverberation, and time-stretching – ensuring the watermark stays intact even after heavy audio manipulation.
Techniques such as adversarial training and latent-space optimization play a key role in striking the perfect balance between invisibility and durability. These methods allow watermarks to survive common hurdles like lossy codecs and automated transformations, all while preserving the original sound quality. Thanks to these advancements, tools like ScoreDetect offer creators and businesses a dependable, non-intrusive way to safeguard their digital audio content.
What are the key challenges in balancing imperceptibility and durability in audio watermarking?
In audio watermarking, the core challenge is finding the right balance between two critical factors: imperceptibility and durability. On one hand, the watermark must be subtle enough to remain undetectable to human listeners. On the other hand, it needs to be durable enough to survive audio processing techniques like compression, noise addition, or re-sampling. Increasing the watermark’s strength can improve its durability but might compromise sound quality. Conversely, a more delicate watermark preserves the audio’s fidelity but becomes easier to distort or remove.
To navigate this challenge, psychoacoustic techniques are often used to embed watermarks in "safe zones" – areas within the audio spectrum that are less noticeable to the human ear. However, this approach may come at the expense of robustness. Cutting-edge methods, such as ScoreDetect’s invisible watermarking, aim to achieve a better balance. By embedding watermarks that are imperceptible yet secure, and incorporating blockchain technology for ownership verification, these advanced techniques ensure the watermark remains intact during standard distribution processes. This approach safeguards audio quality while providing reliable proof of ownership.
How do adaptive embedding techniques enhance audio watermarking?
Adaptive embedding enhances audio watermarking by tailoring the watermark’s placement and intensity to align with the unique features of the audio. This method takes advantage of psychoacoustic masking, embedding data in areas of the audio where human hearing is less sensitive, which helps preserve the overall sound quality.
By focusing on specific frequency ranges, time regions, or signal parts that can handle slight alterations, adaptive techniques create watermarks that are tougher to detect, more durable, and harder to remove, all while keeping the original audio intact.

