Audio watermarking is a powerful tool to combat piracy in streaming platforms. By embedding hidden markers into audio signals, it allows content owners to trace leaks, verify ownership, and secure revenue streams. Unlike encryption, watermarks remain intact even after recording or re-encoding, making them a reliable solution for tracking misuse.
Key Takeaways:
- What It Does: Embeds invisible markers in audio to track content and verify ownership.
- How It Works: Uses techniques like Spread Spectrum Watermarking (SSW) to make markers inaudible but resistant to tampering.
- Applications: Used in music, podcasts, audiobooks, live broadcasts, and cinema to trace leaks and deter piracy.
- Detection: Specialized tools extract watermarks from altered audio to identify the source of leaks.
- Advanced Features: Real-time embedding for live streams, traitor tracing, and integration with AI for piracy detection.
Audio watermarking is essential for protecting streaming content against piracy and ensuring rightful ownership.
UOC‘s Audio Watermarking System, High-fidelity recovery under extreme conditions

How Audio Watermarking Works
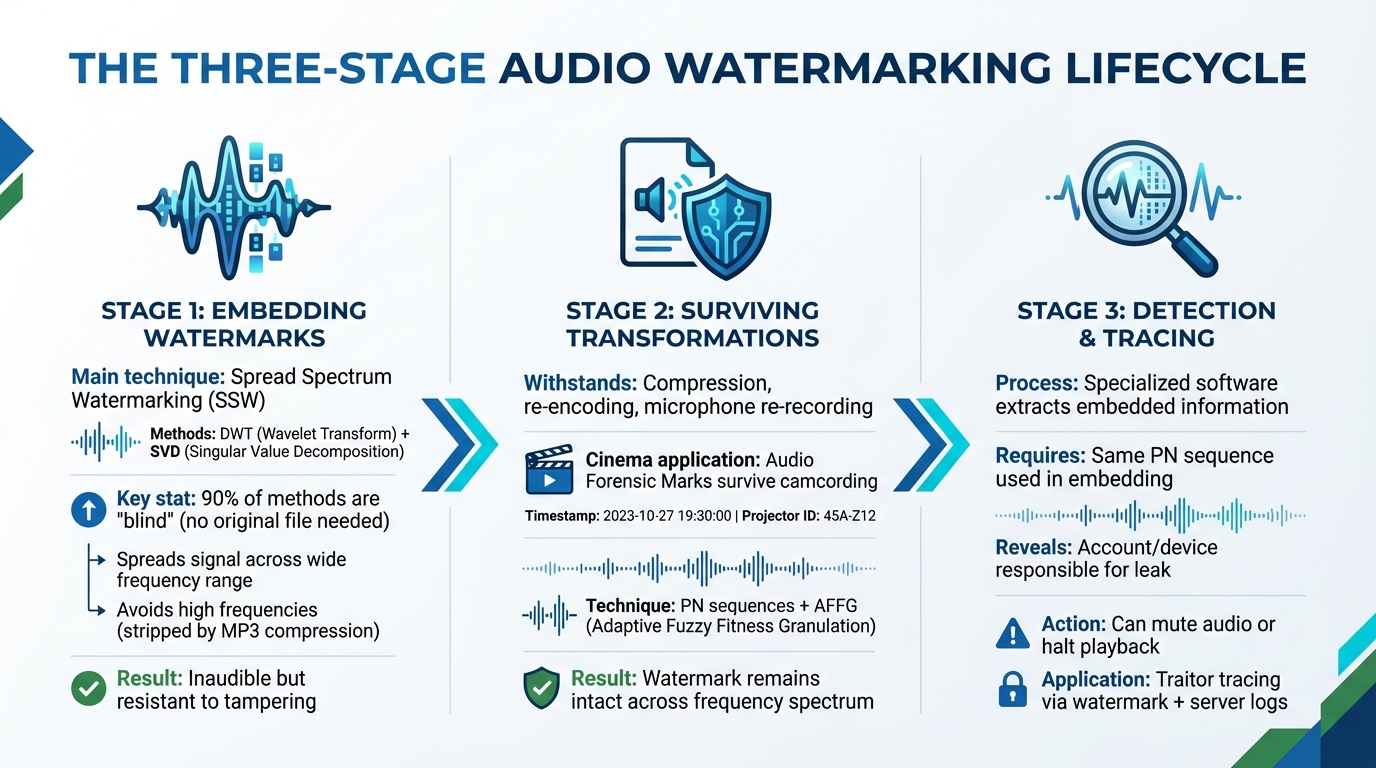
How Audio Watermarking Works: Embedding, Survival, and Detection Process
Embedding Watermarks in Audio Files
Audio watermarks are embedded by taking advantage of the way humans perceive sound. Since our hearing isn’t highly sensitive to subtle changes, these watermarks can be added in a way that keeps them hidden while ensuring the original audio remains clear and undistorted [4]. A popular method for this is Spread Spectrum Audio Watermarking (SSW), which spreads a narrow signal across a wide frequency range. This approach makes the watermark nearly impossible to hear by dispersing its energy across multiple frequencies [1].
To embed these watermarks, developers often use advanced mathematical techniques like the Wavelet Transform (DWT) and Singular Value Decomposition (SVD). DWT breaks audio into low-frequency components (which carry most of the sound’s essence) and high-frequency details, while SVD works by embedding the watermark into the singular values of the audio’s matrix representation. This balance ensures the watermark is both undetectable to listeners and resistant to tampering [4]. A scaling factor is used to fine-tune the watermark – making it strong enough for detection but faint enough to remain inaudible [4].
"The use of DWT and SVD provided with the perceptually transparent embedding of a large amount of data and good robustness."
- Carlos Jair Santin-Cruz, Ph.D. Candidate, National Institute of Astrophysics, Optics and Electronics [4]
Interestingly, most modern audio watermarking methods – about 90% – are "blind." This means they can detect watermarks without needing the original, unaltered audio file for comparison [4]. High-frequency ranges are generally avoided during embedding since processes like MP3 compression often strip them away [4]. In the next section, let’s look at how these watermarks hold up under common audio manipulations.
Surviving Common Audio Transformations
Audio watermarks are built to endure a variety of changes, including compression and even re-recording via microphones. Since the watermark’s signal is spread across multiple frequencies, removing it entirely would require adding disruptive noise across the entire audio spectrum, which is impractical [1].
In digital cinema, Audio Forensic Marks are designed to withstand camcording – when someone records audio in a theater using a microphone. These marks include a timestamp and a unique identifier tied to the specific projector, allowing investigators to trace illegal recordings back to the theater and time they were made [1]. Advanced techniques, such as pseudonoise (PN) sequences and Adaptive Fuzzy Fitness Granulation (AFFG), make it easier to recover watermarks even when the audio has been altered, ensuring the watermark remains intact for identification [1].
Detection and Tracing Methods
Detecting watermarks involves specialized software that scans audio files to extract the embedded information. This process requires access to the same PN sequence used during the watermarking process [1]. On streaming platforms, if pirated content surfaces online, the watermark can reveal which account or device was responsible for the leak [1].
Detection tools are designed to work across various platforms, analyzing audio streams for hidden markers. Some consumer devices and software can even act on detected watermarks by muting audio or halting playback to prevent unauthorized use [1].
"Information obtained from watermarks in unauthorized copies, along with logs generated by media blocks, can be examined as part of an investigation to identify the source of the recordings, called traitor tracing."
Applications of Audio Watermarking in Streaming
Music and Podcast Distribution
Platforms for music and podcasts rely on audio watermarking to safeguard copyright and track unauthorized sharing. By embedding unique identifiers across various frequency bands, these watermarks are practically undetectable to listeners and resistant to removal without harming audio quality[1]. If a song or podcast surfaces on an unauthorized platform, the embedded watermark can reveal the source of the leak, whether it’s a specific distribution point or a user account – a method known as traitor tracing[1].
Some streaming platforms go a step further by using interactive watermarks that can enforce playback restrictions when unauthorized use is detected. These techniques are also applied to other formats, such as audiobooks and live broadcasts.
Audiobooks and Live Broadcasts
Audiobooks and live broadcasts present distinct piracy challenges, which real-time audio watermarking is well-equipped to address. During live broadcasts, systems embed unique identifiers and timestamps directly into the audio stream. If the content is recorded and redistributed without permission, these watermarks enable investigators to trace the incident back to a specific account or session[1]. This capability acts as a strong deterrent, especially against insider leaks.
For instance, integrated watermark detectors can automatically mute or flag unauthorized recordings. For audiobook publishers, watermarks remain intact even after re-compression, ensuring ownership can always be verified[1][2].
Cinema and Anti-Camcording Measures
In the fight against camcorder piracy, which costs the film industry around $6.1 billion annually, audio watermarking plays a critical role[5]. Digital cinema systems, adhering to the Digital Cinema Initiatives (DCI) specifications, embed Audio Forensic Marks into soundtracks in real time. These marks include details like the projector ID and timestamp, allowing investigators to trace unauthorized recordings back to the exact theater and showtime[1].
"Watermarking does not stop unauthorized recordings or their distribution, though it may deter unauthorized copying by those aware of the watermarking process."
- Digital Cinema Initiatives, LLC[1]
Advanced systems can even estimate a camcorder’s location within about 1.6 feet by analyzing signal delays from multiple speakers[5]. Unlike purely digital protections, these audio watermarks survive the journey through theater speakers and re-recording by microphones, making them particularly effective against pre-release piracy. This durability ensures that watermarking remains a reliable tool in protecting cinematic content.
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Integrating Audio Watermarking in Your Streaming Workflow
To strengthen content security, it’s essential to incorporate effective watermarking techniques into your streaming workflow. Here’s how you can do it.
Selecting the Right Watermarking Solution
The type of watermarking solution you choose should align with your content and distribution methods. For music streaming, you’ll need watermarks that can endure re-encoding and compression. On the other hand, live broadcasts demand real-time insertion tools capable of embedding forensic marks with unique identifiers and timestamps. These are crucial for tracking leaks back to their source.
A good watermarking solution strikes a balance between being undetectable to listeners and resilient against transformations like format changes or analog re-recording. Whether you’re dealing with pre-recorded files or live streams, focus on solutions that seamlessly integrate into your workflow while meeting these requirements.
Once you’ve identified the right tool, the next step is embedding it into your system and rigorously testing its performance.
Embedding and Testing Watermarks
The process of embedding watermarks varies depending on the content type. For pre-recorded content, watermarks are typically added during the encoding phase before distribution. In live streaming, server-side tools generate unique Audio Forensic Marks at the point of delivery. These marks assign recipient-specific identifiers to every stream, making it easier to trace leaks[1].
After embedding, test the watermarks for both imperceptibility and robustness. This involves simulating scenarios like re-encoding, adding noise, or analog re-recording to ensure the watermark remains intact. As Jonathan Friend, CEO of Friend MTS, highlights:
"You shouldn’t do subscriber-level watermarking until you have DRM robustly in place"[3].
Remember, watermarking is most effective when combined with other security measures, forming a comprehensive defense strategy.
Monitoring and Enforcement
Once watermarks are embedded, continuous monitoring is key. Automated systems scan for unauthorized copies, extracting identifiers to trace leaks. Platforms like ScoreDetect enhance this process by combining invisible watermarking with AI-powered discovery. Impressively, it achieves a 95% success rate in bypassing preventive measures and generates automated takedown notices with over 96% effectiveness.
Enforcement involves three steps: detection, verification, and action. When pirated content is detected, the system extracts the watermark and cross-references it with server logs to confirm the breach. For cinema releases adhering to Digital Cinema Initiatives (DCI) standards, this process can pinpoint not just the theater but also the specific projector and timestamp responsible for the leak[1]. Additionally, ScoreDetect’s blockchain integration records content checksums, creating tamper-proof proof of ownership. This becomes invaluable when pursuing legal action against repeat infringers.
ScoreDetect: Digital Content Protection for Streaming Platforms
Streaming platforms face unique challenges when it comes to protecting their content. With the global audio streaming market expected to surpass $120 billion by 2026 and piracy losses in entertainment ranging between $40 billion and $97 billion annually [6][7], basic security measures like watermarking simply aren’t enough. That’s where ScoreDetect comes in. This solution from InCyan combines invisible watermarking, AI-driven detection, and blockchain validation to safeguard streaming audio at every stage of its journey.
Invisible, Non-Invasive Watermarking
ScoreDetect uses spread spectrum watermarking (SSW) technology, which embeds watermarks across multiple frequency bands. These watermarks are invisible to listeners but tough enough to withstand attacks like compression or format changes [6]. The best part? The watermarking process happens automatically during upload or transcoding through API integration, eliminating the need for manual intervention [6][8]. This ensures your audio quality remains untouched while setting the stage for effective detection.
AI-Driven Piracy Detection and Takedown
With AI pattern recognition, ScoreDetect scans external platforms – like social media and torrent sites – for unauthorized copies. It identifies these with a 95% success rate, even bypassing common prevention tactics [7]. Once a violation is spotted, the system gathers metadata to trace the source of the leak and sends automatic takedown notices to offending platforms. This approach has led to a 96% success rate in takedowns and sped up copyright violation resolutions by 30% [10].
Blockchain Integration for Copyright Validation
To bolster content security, ScoreDetect uses blockchain technology to record an audio checksum on an immutable ledger. This creates undeniable proof of ownership without storing the actual audio files [9][10]. The decentralized ledger provides a transparent transaction history, making ownership claims clear and enforceable in legal disputes [10]. Acting like a "digital fingerprint", this feature strengthens your case against repeat offenders and adds an extra layer of protection to your content.
Conclusion
Audio watermarking has become an essential tool for streaming platforms aiming to protect their content and maintain revenue. By embedding hidden markers into audio signals, this technology ensures ownership can be proven even after common audio modifications – something encryption alone cannot achieve. As Carlos Jair Santin-Cruz, Ph.D. candidate in Electronics at INAOE, explains:
"Audio watermarking has been introduced to give authors and owners control over the use of audio signals" [4].
One popular approach, spread spectrum watermarking, embeds markers by distributing the signal across multiple frequency bands. This method makes removal nearly impossible without degrading audio quality [1]. Its balance of durability and sound integrity has made it a cornerstone of traitor tracing systems in digital cinema and streaming services.
Beyond its resilience, watermarking also enables active content protection. Automated systems can detect unauthorized watermarks and block playback, while Digital Cinema Initiatives use Audio Forensic Marks to pinpoint leaks to specific projectors and timestamps [1]. This shifts watermarking from a passive identification tool to a proactive piracy deterrent.
For platforms managing vast libraries, integrated solutions simplify protection workflows. For instance, ScoreDetect combines invisible watermarking with AI-powered detection and blockchain validation, automating the process of identifying and removing unauthorized content with impressive accuracy.
Ultimately, audio watermarking is indispensable for streaming platforms. It provides the technical backbone for large-scale copyright enforcement, ensuring content ownership, revenue, and creative rights remain secure.
FAQs
What is the difference between audio watermarking and encryption for protecting streaming content?
Audio watermarking and encryption are two distinct tools used to safeguard streaming content, each with its own strengths.
Audio watermarking works by embedding invisible identifiers directly into the audio signal. These identifiers are like digital fingerprints – they allow content owners to track unauthorized use, confirm ownership, and protect their work without altering the sound quality. The best part? These identifiers stay intact even after the audio undergoes compression, filtering, or other modifications.
Encryption, on the other hand, focuses on securing content by converting it into an unreadable format. To access the content, users need a decryption key. This method is excellent for restricting access during transmission or storage, but once the file is decrypted, encryption can’t help with tracking or identifying the content.
When used together, these methods form a powerful defense. Encryption ensures the secure delivery of content, while audio watermarking provides ongoing protection and traceability after the content has been distributed.
What makes embedding watermarks in live broadcasts challenging?
Embedding watermarks in live broadcasts comes with unique hurdles, mainly because of the need to process everything in real-time. The watermark has to be invisible to the audience but still strong enough to withstand the challenges of streaming, such as compression, noise, and transmission distortions. On top of that, unpredictable elements like interference or background noise can further complicate its reliability.
Another major challenge is maintaining low latency. Watermarking needs to happen quickly enough to avoid any delays or dips in the broadcast’s quality. Live streams also deal with constantly shifting conditions and platform differences, which makes it tricky to ensure the watermark stays intact and recognizable across various devices and networks. Addressing these challenges requires highly efficient and advanced techniques tailored for the demands of live streaming.
How does AI improve the detection of unauthorized audio content?
AI plays a key role in spotting unauthorized audio content by leveraging advanced algorithms designed to detect hidden watermarks embedded in audio files. These watermarks are crafted to be inaudible to human listeners but easily identifiable by detection systems. Thanks to machine learning and deep learning methods, these systems can recognize watermarks even after the audio undergoes transformations like compression or added noise.
Another advantage of AI is its ability to handle large amounts of audio efficiently. Using pattern recognition, it can pick up subtle, nearly imperceptible watermarks that take advantage of the natural limits of human hearing. This makes it easier for content creators to quickly and accurately track unauthorized use, providing stronger copyright protection and helping to curb piracy in streaming and broadcast platforms.

