Invisible watermarks are hidden signals embedded in images to verify ownership or detect AI-generated content. However, diffusion models, like those used in advanced AI systems, can easily bypass these watermarks. Attackers can remove or fake watermarks with a success rate of over 97%, undermining content protection.
To counter this, researchers have developed advanced methods like ZoDiac, WaDiff, and ROBIN. These techniques embed watermarks deeper into the creation process or strengthen them against tampering. Tools like ScoreDetect add extra layers of protection, combining watermarks with blockchain verification and AI-powered enforcement to safeguard digital assets.
Key findings:
- Diffusion models can erase or forge watermarks with minimal effort.
- Defense methods focus on embedding watermarks during image generation for better durability.
- Tools like ScoreDetect integrate watermarking with blockchain to enhance security.
These strategies highlight the ongoing battle to protect digital content from evolving AI threats.
PT-Mark: Invisible Watermarking for Text-to-image (Apr 2025)
How Diffusion Models Attack Invisible Watermarks
Diffusion models have emerged as formidable tools for targeting invisible watermarks, employing methods that either inject fake watermarks into clean images (forgery) or strip watermarks from protected content (removal). These approaches manipulate the diffusion process itself, treating watermarks as patterns that can be learned, altered, or erased. Let’s dive into how these attacks work and their broader implications.
Common Attack Techniques
One standout framework in this field is DiffForge, which has proven highly effective. DiffForge works by estimating the distribution of watermarks from a small dataset of watermarked images and injecting these patterns into clean images. This method has achieved a 97% success rate against Amazon’s Titan text-to-image model’s watermark detection system [1].
The technique’s secret lies in shallow inversion, a process that transforms clean images into latent variables with minimal reconstruction errors. This ensures the original image quality is preserved while creating room to inject watermarks during the denoising phase, resulting in PSNR values exceeding 29.06dB [1].
"Attackers can leverage unrelated models, even with different latent spaces and architectures (UNet vs DiT), to perform powerful and realistic forgery attacks." – Andreas Müller, Researcher, Ruhr University Bochum [5]
Another method, Imprinting, has demonstrated the ability to transfer watermarks from AI-generated images onto unrelated photographs. For example, it successfully imprinted watermarks onto a moon landing photo, causing detection systems to misattribute the image to specific providers. This approach improved forgery performance by 68% compared to older methods [1].
Lastly, reprompting attacks take a different route by reversing the noise vector of a watermarked image. This generates new content that still carries the original watermark, effectively spreading the watermark signal to unrelated images [5].
Effects on Watermark Performance
These attack methods have far-reaching consequences for watermarking systems. First, they significantly reduce detection accuracy. For instance, DiffForge deceived open-source watermark detectors with a 96.38% success rate, all while maintaining high visual quality that makes the manipulations nearly invisible to human eyes [1].
Second, these attacks work in "no-box" scenarios, meaning attackers don’t need access to the watermarking algorithm or paired datasets. A small set of watermarked images is enough to estimate patterns and execute successful forgeries [1].
The implications go beyond technical performance. These attacks not only forge or remove watermarks but also undermine the very purpose of watermarking systems. Forgery attacks can falsely attribute harmful or illegal content to innocent users or organizations, creating legal and ethical risks. For example, in real-world tests, Amazon’s Responsible AI detection API mistakenly classified forged images as authentic, exposing how these vulnerabilities could erode trust in AI content accountability frameworks [1].
Defense Methods for Protecting Invisible Watermarks
To tackle the vulnerabilities exploited by diffusion models, researchers are embedding watermarks more deeply into the image creation process. As attacks on diffusion models become increasingly advanced, these strategies aim to make watermarks harder to forge or remove. By integrating watermarks into the generation process, training systems to resist adversarial manipulation, and leveraging the unique features of diffusion models, these methods strengthen watermark protection.
ZoDiac: Watermarking Defense Against AI Attacks
The ZoDiac method uses the trainable latent space within diffusion models to create watermarks that naturally resist tampering. Unlike traditional approaches that add watermarks after an image is created, ZoDiac embeds them directly into the diffusion model’s denoising process. This integration enhances the watermark’s durability against aggressive removal attempts.
"We hypothesize that the reciprocating denoising process in diffusion models may inherently enhance the robustness of the watermark when faced with strong attacks and validate the hypothesis." – Lijun Zhang, Lead Author, arXiv:2401.04247 [2]
The results back this up: ZoDiac achieves a watermark detection rate above 98%, even under attack, while keeping the false positive rate under 6.4% [2]. This is a significant improvement, especially when compared to traditional systems where detection accuracy drops to around 67.92% during fine-tuning attacks [7]. Moving forward, the WaDiff method builds on ZoDiac’s foundation by embedding watermarks during the image generation process.
WaDiff: Watermark-Conditioned Diffusion Models
WaDiff (Watermark-Conditioned Diffusion) changes the game by embedding watermarks as part of the image creation process instead of treating them as an afterthought. This generative watermarking approach integrates the watermark into the longer sampling tracks and multimodal structures typical of diffusion models [6].
One of WaDiff’s strengths lies in its efficiency. The watermark encoder is only active during training and is discarded during inference (image generation) [3]. As a result, the system doesn’t slow down image creation while still providing robust protection. By embedding watermarks at the generation level, WaDiff ensures the patterns can survive AI-based removal attempts without compromising image quality.
ROBIN Method: Adversarial Watermark Protection
While methods like ZoDiac and WaDiff focus on embedding watermarks during the generation process, the ROBIN method takes a different approach by countering targeted adversarial attacks. These attacks often use machine learning classifiers to detect and remove watermarks through pixel manipulation [7]. ROBIN addresses this by employing adversarial training, making the watermarks "invisible" to these classifiers while keeping the image content visually intact.
In March 2025, researchers from the State Key Laboratory of Blockchain and Data Security at Zhejiang University demonstrated the DiffForge attack on Amazon’s Titan text-to-image model. The forged images bypassed Amazon’s watermark detection API, being confidently classified as watermarked. This attack improved forgery performance by 68% compared to previous methods [1].
"Indistinguishability alone does not necessarily guarantee resistance to adversarial removal." – De Zhang Lee et al., National University of Singapore [8]
ROBIN also addresses "boundary leakage", a vulnerability where watermarking schemes inadvertently reveal the locations of watermarked regions. This flaw allows attackers to remove watermarks with up to 15x less distortion than standard attacks [8]. By making it exponentially harder for attackers to locate and manipulate embedded patterns, ROBIN significantly raises the bar for adversarial removal attempts.
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Comparing Defense Methods
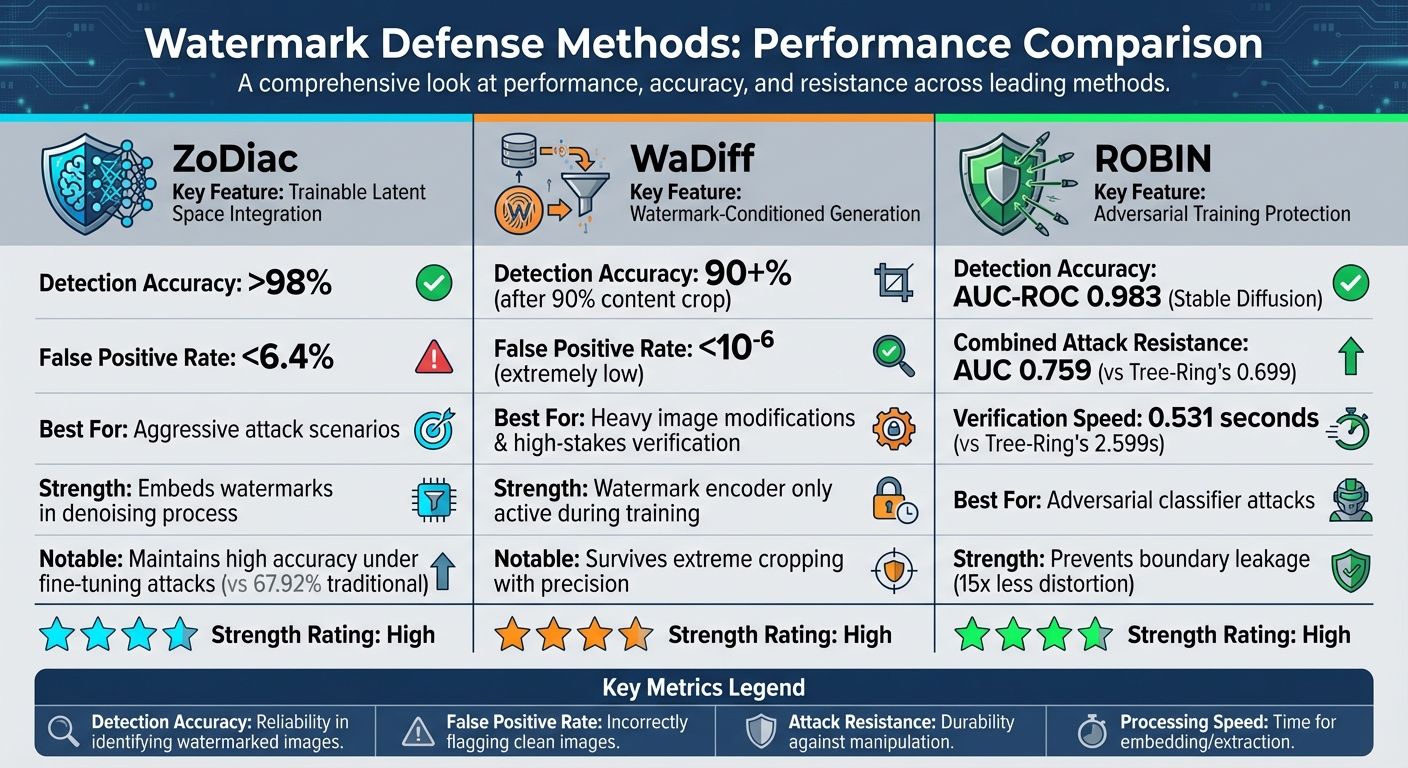
Comparison of Watermark Defense Methods: ZoDiac, WaDiff, and ROBIN Performance Metrics
Performance Metrics
When looking at watermark defense methods, there are four main metrics that help determine their effectiveness in practical applications:
- Detection accuracy: This shows how reliably a system can identify watermarked images. The higher the accuracy, the better the protection.
- Image quality: Measured using tools like Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Inception Score (IS), and Fréchet Inception Distance (FID), this ensures watermarks are invisible while keeping the original image intact.
- Attack resistance: This tests how well watermarks hold up against common manipulations, such as cropping, compression, or AI-driven forgery attempts.
- False positive rate (FPR): This measures how often clean images are incorrectly flagged as watermarked. A lower FPR means more reliable verification.
Additionally, processing speed – the time it takes to embed or extract watermarks – is crucial when dealing with large libraries of images. These metrics provide a foundation for comparing defense strategies and selecting the best approach to counter threats from diffusion models.
Side-by-Side Comparison
When comparing the three defense methods, each demonstrates specific strengths depending on the attack scenario:
- ZoDiac: This method shines in scenarios with aggressive attacks, maintaining over 98% detection accuracy while keeping the false positive rate below 6.4% [2]. By leveraging a trainable latent space approach, ZoDiac balances high image quality with strong resistance to diffusion-based manipulations.
- WaDiff: Known for its resilience to heavy image modifications, WaDiff is particularly effective in high-stakes verification. Researchers Pierre Fernandez and colleagues note, "Stable Signature works even after the images are modified… it detects the origin of an image generated from a text prompt, then cropped to keep 10% of the content, with 90+% accuracy at a false positive rate below $10^{-6}$" [4]. This extremely low false positive rate makes it a standout choice for scenarios requiring precise verification.
- ROBIN: Taking a different approach, ROBIN focuses on adversarial protection. It achieves an average AUC-ROC of 0.983 for Stable Diffusion under various attacks [9][10]. It’s also faster, with a verification speed of about 0.531 seconds, compared to Tree-Ring’s 2.599 seconds [9][10]. ROBIN performs well under combined attacks too, achieving an AUC of 0.759 against three simultaneous manipulations, outperforming Tree-Ring’s 0.699 [10].
Each method targets different threat models, so the best choice depends on your specific needs – whether it’s defending against forgery, withstanding major image changes, or countering adversarial classifiers.
Using ScoreDetect for Digital Content Protection
ScoreDetect steps in to address the gaps in invisible watermarking by offering a multi-layered approach to digital content security. Created by InCyan, this tool combines advanced invisible watermarking with blockchain verification to safeguard your digital assets effectively.
ScoreDetect’s Watermarking Technology
At its core, ScoreDetect uses an invisible watermarking system to embed traceable data into digital files without compromising their quality. These watermarks are designed to withstand common manipulations like cropping or compression, making them incredibly resilient against tampering.
What sets ScoreDetect apart is its integration with blockchain technology. Each file’s cryptographic checksum is recorded on an immutable ledger, creating a tamper-proof record of ownership. This ensures that the authenticity of a file can be verified without needing to store the actual content. Together, these features provide a solid foundation for protecting digital assets throughout their entire lifecycle.
How ScoreDetect Strengthens Watermark Defense
ScoreDetect doesn’t stop at embedding watermarks. It adds multiple layers of protection to secure your assets from start to finish. Here’s how it works:
- The Discover feature uses intelligent web scraping to scour the internet for unauthorized copies of your content. Impressively, it bypasses most prevention measures with a 95% success rate.
- After identifying potential infringements, the Analyse feature compares the discovered content with your protected assets to provide hard evidence of unauthorized use.
- To top it off, ScoreDetect automates enforcement, achieving a 96% success rate in takedowns of infringing content.
By combining invisible watermarking, AI-powered detection, blockchain verification, and automated takedowns, ScoreDetect offers a robust defense against even the most advanced threats, like diffusion model attacks.
ScoreDetect in Different Industries
ScoreDetect’s versatility makes it a powerful tool across various sectors:
- Media and Entertainment: Protects visual content from unauthorized sharing while using blockchain to enforce copyright.
- Ecommerce: Shields product images and videos with invisible watermarks to prevent misuse.
- Legal Sector: Blockchain timestamping helps establish document creation dates and ownership, particularly in intellectual property cases.
- Content Publishing: A WordPress plugin automatically tracks published or updated articles, creating blockchain-verified ownership records that also enhance SEO by boosting E-E-A-T signals.
- Marketing and Advertising: With Zapier integration, ScoreDetect connects seamlessly to over 6,000 web apps, simplifying workflow automation for agencies.
Conclusion
Modern AI threats require active watermarks that are strategically embedded into content. As Huayang Huang points out, current watermarking methods strike a balance between being robust and remaining concealed by carefully managing watermark strength [9].
Using insights from recent attacks, advanced defenses now focus on embedding watermarks during critical diffusion steps, leveraging adversarial optimization to improve resilience. For example, methods like ROBIN achieve an impressive AUC of 0.983 with verification times as quick as 0.531 seconds. Similarly, ZoDiac maintains over 98% detection accuracy while keeping false positives under 6.4% [2] [10].
However, the threat landscape continues to evolve. Forgery attacks are now capable of injecting fake watermarks with a success rate exceeding 97%, posing serious risks to reputations and digital integrity [1]. This highlights the need for comprehensive defenses that include ongoing monitoring, verification, and enforcement.
ScoreDetect addresses these challenges with a multi-layered defense system. It combines invisible watermarking, blockchain-based verification, and AI-driven enforcement. Developed by InCyan, this system achieves 95% detection success and 96% automated takedown efficiency, offering robust protection for digital assets across industries like media, ecommerce, legal, and publishing.
FAQs
Why are diffusion models so effective at bypassing invisible watermarks?
Diffusion models are particularly skilled at sidestepping invisible watermarks by studying and replicating their patterns. Using methods like shallow inversion, they introduce noise during the early stages of the diffusion process. This added noise disrupts the watermark’s structure, making it harder for detection systems to confirm or recognize the watermark’s presence.
By mimicking the watermark’s distribution and merging it with noise, these models can either degrade or forge watermarks with impressive accuracy. This capability enables them to alter digital assets while avoiding detection by conventional watermark verification tools.
How do ZoDiac, WaDiff, and ROBIN differ in protecting invisible watermarks?
When it comes to embedding and protecting invisible watermarks in diffusion models, ZoDiac, WaDiff, and ROBIN each bring their own strategies to the table.
- ZoDiac employs adversarial optimization to embed watermarks during the intermediate stages of diffusion. This ensures the watermarks remain detectable, even after attempts to tamper with them significantly.
- WaDiff takes a different route by encoding ownership details directly into generated images. Its focus is on creating watermarks that are imperceptible but effective in preventing unauthorized use of generative diffusion models.
- ROBIN, on the other hand, actively embeds watermarks during the diffusion process using optimized prompts. It strikes a balance between invisibility and durability, producing watermarks that are both hard to detect and resistant to degradation, all without leaving visible artifacts.
To sum up, ZoDiac prioritizes robustness against tampering, WaDiff zeroes in on ownership verification, and ROBIN blends invisibility with strength for a well-rounded approach to watermark protection.
How does ScoreDetect use blockchain technology to protect digital content?
ScoreDetect uses blockchain technology to generate a checksum for your digital content. This checksum acts as verifiable proof of ownership, ensuring copyright protection without needing to store the actual files. Essentially, it creates an unchangeable record that confirms your content’s originality.
With blockchain, ScoreDetect strengthens security and provides clarity, simplifying the process of proving ownership in cases of disputes or unauthorized use.

