NFTs are reshaping digital ownership but are also being exploited for money laundering due to their pseudonymous nature, borderless transactions, and unpredictable valuations. Criminals use tactics like wash trading, self-laundering, and layering to move illicit funds. In 2024, the U.S. Treasury flagged NFT platforms as vulnerable, citing weak controls and regulatory gaps.
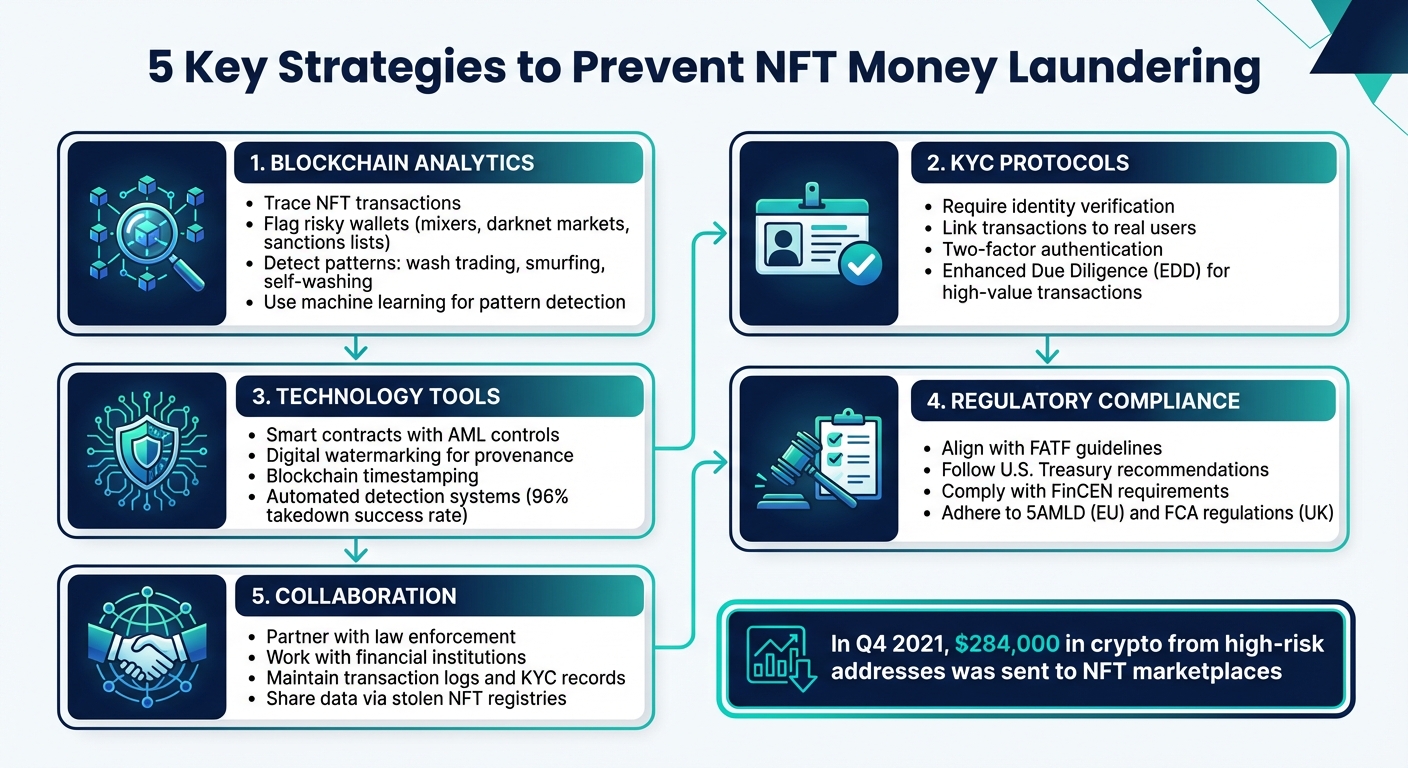
Key Solutions:
- Blockchain Analytics: Trace NFT transactions, flag risky wallets, and detect patterns like wash trading or smurfing.
- KYC Protocols: Require identity verification to link transactions to real users.
- Technology Tools: Use smart contracts, digital watermarking, and automated systems to block fraud and track provenance.
- Regulatory Compliance: Align with AML frameworks like FATF guidelines and U.S. Treasury recommendations.
- Collaboration: Work with law enforcement and financial institutions to freeze accounts and disrupt laundering schemes.
Platforms that combine these measures can strengthen security, meet regulatory standards, and build user trust while combating illicit activities in the NFT space.
5 Key Strategies to Prevent NFT Money Laundering
Money Laundering Risks in NFTs
How NFTs Enable Money Laundering
NFTs have become a magnet for money launderers, blending the anonymity of cryptocurrency transactions with the unpredictable valuation of digital art [8]. The decentralized nature of these platforms allows users to create wallets and trade without the need for identity verification, giving criminals the cover of pseudonyms [2]. Add to that the ease of transferring NFTs across borders, and it becomes a challenge to freeze or seize these assets [2]. The fluctuating prices of NFTs further muddy the waters, making suspiciously large payments look like speculative investments [7]. These vulnerabilities have given rise to a range of laundering techniques.
Common Money Laundering Tactics in NFTs
One of the most common tactics is wash trading, where criminals use multiple wallets to repeatedly buy and sell the same NFT. This artificially inflates its value, creating the illusion of high demand. In 2021, Chainalysis identified hundreds of cases of NFT wash trading, with traders driving up prices artificially, often ending up with net losses due to transaction fees [6]. This method not only launders illicit funds but also misleads potential buyers by distorting market trends.
Another method is self-laundering – often referred to as closed-loop schemes. Here, an individual mints an NFT and then trades it among wallets they control, gradually driving up its price. Eventually, the NFT is sold at a high value, masking the illicit origins of the funds [4][5].
Criminals also use layering techniques to obscure the trail of illegal money. This involves employing tools like mixers, tumblers, multiple wallets, and cross-chain transactions. These steps make it increasingly difficult to track the funds back to their original, unlawful source [2][5].
The scale of NFT-related money laundering is staggering. In just the fourth quarter of 2021, around $284,000 in cryptocurrency linked to high-risk addresses – some with sanctions concerns – was funneled into NFT marketplaces. A significant portion of these funds also came from wallets tied to scams [6]. And these figures likely only scratch the surface of the illicit activity happening in the NFT ecosystem.
Blockchain Analytics and Transaction Monitoring
Using Blockchain Transparency to Detect Suspicious Activity
Public blockchains like Ethereum keep a record of every NFT transaction, making it possible for investigators to track wallet activity and connect addresses to real-world entities [5][7][6]. Unlike traditional financial systems, where transaction details are often hidden, blockchain data is open to anyone with the right tools to analyze it.
Analytics platforms make good use of this transparency. These tools group addresses, flag risky wallets – such as those linked to mixers, darknet markets, sanctions lists, or stolen funds – and identify patterns that suggest NFT money laundering. This could include activities like wash trading, smurfing (where transactions are kept under reporting thresholds), or self-washing schemes where the same NFT is traded repeatedly within a closed loop [2][5][6].
Machine learning plays a critical role here. Since NFT money laundering is a relatively new issue, there isn’t much institutional knowledge to rely on for traditional detection methods. Machine learning can quickly spot suspicious behaviors, such as circular flows of funds across multiple wallets or repeated trades of the same NFT between related addresses. These algorithms analyze blockchain data at a scale and speed that would be impossible for manual efforts [5][7][9].
While these tools and techniques are powerful, they also come with significant challenges.
Limitations of Blockchain Analytics
Though blockchain transactions are transparent, the pseudonymous nature of wallets means that owner identities remain hidden unless Know Your Customer (KYC) data is available [5][8]. Criminals often exploit this by using mixers, privacy coins, or cross-chain bridges to obscure their tracks.
Another issue is that address labeling relies on databases that are often incomplete. The gap between on-chain data (blockchain records) and off-chain data (real-world identities) makes it even harder to pinpoint individuals [5][7][8]. Adding to the complexity is the decentralized and global nature of NFT platforms, which allows criminals to take advantage of jurisdictional differences to avoid legal consequences [3].
These challenges highlight the need for blockchain analytics to be part of a broader strategy. Combining these tools with strong KYC processes and international regulatory cooperation is essential to effectively tackle NFT money laundering.
KYC and Customer Due Diligence
KYC and Identity Verification for NFT Marketplaces
Many NFT platforms fall short when it comes to implementing proper Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, leaving them vulnerable to misuse [5]. Without identity verification, criminals can exploit the anonymity of blockchain transactions to move funds undetected [2][3]. To build a secure marketplace, combining KYC with blockchain analytics is essential.
The U.S. Treasury has flagged this issue, noting that "some NFT firms and platforms lack appropriate controls to mitigate risks to market integrity and to combat money laundering and terrorist financing, and sanctions evasion" [7]. This lack of oversight has allowed illicit funds to flow through platforms with weak compliance measures.
Introducing mandatory KYC procedures would require users to verify their identities before conducting transactions, much like how regulated cryptocurrency exchanges operate [1][2]. This could involve steps like two-factor authentication to secure accounts and protect verified identities [1]. The aim is clear: every transaction should be tied to a verified user, reducing the anonymity that makes NFTs appealing for money laundering [2].
Regulators are tightening the reins. Both the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and the U.S. Treasury classify NFT platforms as Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), potentially subjecting them to regulations under FinCEN, including anti-money laundering (AML) and countering the financing of terrorism (CFT) requirements [5][6]. In the European Union, the Fifth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (5AMLD) extends KYC obligations to virtual currency providers and art dealers for transactions exceeding €10,000 [5]. Similarly, the UK’s Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing (Amendment) Regulations 2019 mandate NFT businesses to register with the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) for proper oversight [5].
By layering identity verification and transaction monitoring, NFT platforms can adopt more sophisticated risk management practices.
Enhanced Due Diligence for High-Value Transactions
Basic KYC measures are just the starting point. For transactions involving higher risks, platforms need to implement Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) to dig deeper into the details [4]. This means scrutinizing the source of funds, the intent behind transactions, and the actual ownership of accounts.
Certain activities should trigger EDD, such as high-value transactions, suspicious trading patterns, sudden spikes in activity from dormant accounts, quick transfers of NFTs to new wallets, rapid currency conversions, or transactions involving jurisdictions with weak AML/CFT controls [2][6]. A risk-based approach helps platforms focus their compliance efforts where they are needed most [4][6]. For instance, a verified user with a clean record buying a $500 NFT poses far less risk than an unverified user from a high-risk region attempting to purchase a $100,000 NFT.
Machine learning plays a crucial role in spotting unusual patterns that traditional systems might miss [5]. Algorithms can quickly detect circular fund flows across multiple wallets or repeated trades involving the same NFT between related accounts, speeding up the identification of suspicious activity [5].
Additionally, NFT platforms should work closely with traditional financial institutions, which often serve as intermediaries for converting fiat currency to cryptocurrency and vice versa [3]. These institutions already have established AML controls, providing critical checkpoints to block illicit funds from entering or leaving the NFT ecosystem [3].
Regulatory Compliance and Collaboration
AML Frameworks and Guidelines for NFTs
As NFTs grow beyond simple collectibles into investment tools or payment methods, global regulators are stepping in to address potential money laundering risks. The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has clarified that platforms facilitating NFT trades in these contexts might be classified as Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) [5].
In the United States, the Department of the Treasury’s 2024 Illicit Finance Risk Assessment on NFTs was a significant milestone. It was the first federal study to focus exclusively on money laundering risks tied to NFTs [7][9]. The report highlighted gaps in some platforms’ anti-money laundering (AML) controls, cybersecurity defenses, and sanctions screening processes.
Meanwhile, European and UK regulations impose comparable AML requirements. NFT platforms in these regions must align their activities with local definitions, whether as VASPs or art market participants. This means implementing risk-based Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols, transaction monitoring, and sanctions screening. These measures not only enhance compliance but also encourage closer collaboration between NFT platforms and regulators.
Working with Law Enforcement and Financial Institutions
Effective AML enforcement in the NFT sector requires collaboration that extends well beyond individual platforms. Since NFT transactions often span multiple countries and rely on traditional financial institutions for converting fiat currencies, combating illicit activity demands a collective effort [3][7]. The U.S. Treasury’s report emphasizes the need for stronger platform controls, advanced blockchain analytics, and better cooperation between the industry and law enforcement [7][9].
To support investigations, platforms must maintain detailed transaction logs, wallet addresses, and KYC records. In cases involving illicit activity, they may also need to freeze or block accounts [2][7].
Banks and payment processors play a critical role in enforcing AML measures. These entities, which handle fiat currency conversions for NFT platforms, are bound by AML and sanctions regulations. They can deny services to platforms that fail to implement adequate safeguards [2][7]. Using blockchain analytics and clear Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) protocols helps platforms maintain banking relationships and avoid being flagged as high-risk.
The importance of these efforts is underscored by data from Chainalysis, which revealed that, in one quarter, approximately $284,000 worth of cryptocurrency linked to sanctioned addresses was sent to NFT marketplaces [6]. Additionally, many suspicious transactions in these marketplaces originate from scam-related wallets or stolen funds. For example, when platforms notice large NFT purchases from wallets tied to ransomware activities, they should notify both their banking partners and relevant Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs). This helps disrupt laundering operations [2][7].
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Technology Tools for NFT Risk Management
Smart Contracts with Built-In AML Controls
Smart contracts can play a crucial role in enforcing anti-money laundering (AML) rules directly on the blockchain, offering automated safeguards. For instance, they can impose per-transaction limits to counter "smurfing", a tactic where criminals break down transactions to avoid detection under reporting thresholds [5]. Imagine a smart contract that automatically blocks any NFT transfer exceeding a specific dollar-equivalent value unless the wallet owner has undergone enhanced verification checks.
Some advanced smart contracts go a step further by integrating oracle feeds from blockchain analytics platforms. These feeds enable real-time address screening and ensure that NFT listings are restricted to wallets with verified Know Your Customer (KYC) attestations [2][4][5][6]. This approach adds another layer of security, complementing other technological measures in the NFT ecosystem.
Digital Watermarking and Blockchain Timestamping
In addition to smart contracts, tools like digital watermarking and blockchain timestamping enhance the security and provenance of NFTs. The U.S. Treasury’s 2024 NFT risk assessment highlighted the need for better tools to identify stolen or fraudulent content [9]. Digital watermarking embeds invisible markers into digital assets, while blockchain timestamping records cryptographic checksums, together creating an unchangeable record of ownership and authenticity [7].
Platforms like ScoreDetect utilize both technologies to safeguard NFTs. They invisibly watermark original media and log a checksum of each file on the blockchain, generating verification certificates almost instantly. This process provides clear proof of authenticity and creation date without storing the actual asset [10]. Marketplaces can then compare new NFT listings against these registered checksums to flag stolen or fraudulent works before they are listed, reducing the prevalence of laundering through counterfeit NFTs.
Automated Detection and Takedown Solutions
Proactive measures are only part of the equation – automated systems are also essential for identifying and removing fraudulent content. Regulatory and legal experts strongly recommend that NFT platforms deploy automated tools to detect and eliminate scam projects or copyright-infringing listings [3][7][9]. These systems often start with web scraping to scan NFT marketplaces and social media channels for suspicious activity. Advanced tools then use perceptual hashing and AI-driven similarity analysis to match media against registered originals, while also cross-referencing on-chain data to identify patterns like wash trading or links to sanctioned wallets [5][6].
When fraudulent listings are flagged, these systems can swiftly generate delisting notices and send them to marketplaces, hosting providers, or search engines. For example, ScoreDetect’s enterprise plan boasts a 96% takedown success rate through automated notifications. It even integrates with over 6,000 web apps via Zapier, streamlining compliance workflows [10]. By shortening the lifespan of fraudulent NFTs, these tools make it harder for bad actors to use them for illicit purposes.
Best Practices for NFT Money Laundering Prevention
Creating Stolen NFT Registries
A centralized database to track stolen or fraudulent NFTs can be a powerful tool in preventing laundering through NFT resales. ComplyAdvantage suggests using the Art Loss Register from the traditional art world as a model for such a registry [1]. These registries should include details like the NFT’s contract address, token ID, wallet addresses, theft date, and current status [1][3][6]. To avoid false reports, platforms need to verify proof of ownership and gather evidence of compromise – such as on-chain transaction records, support tickets, or law enforcement case numbers – before flagging an NFT [1][7]. When integrated into marketplace checks, flagged tokens can be automatically blocked from being sold or transferred. This system works best when platforms collaborate by sharing standardized data formats and APIs [3][7][9]. Alongside these technical measures, educating users can further help mitigate risks.
User Education and Awareness
Educating users about scams and warning signs is another critical layer of protection, as noted in the U.S. Treasury’s 2024 NFT risk assessment [3][7]. NFT platforms should teach users how to identify red flags, such as receiving off-platform pressure, requests to use privacy coins, unsolicited messages containing suspicious links, or prompts to disable security features [2][3][7]. Educational materials should also shed light on how NFTs can be misused for money laundering – whether through self-purchases to legitimize illicit funds, hacked wallets, or selling stolen intellectual property [1][2][3]. U.S.-specific guidance should direct users on reporting suspicious activities to agencies like FinCEN, the FBI, or IRS-CI, while also explaining the legal consequences of engaging in fraudulent schemes [5][7]. Regular updates through blogs, in-app banners, or short training modules can keep users informed about new laundering tactics as they emerge [2][3][7].
Updating AML Strategies Over Time
Anti-Money Laundering (AML) measures must evolve continuously to address new risks. Platforms should regularly update their AML controls by conducting annual risk assessments, monitoring regulatory changes, and refining transaction rules [4][5][6][7]. A structured governance process can help link regulatory developments and emerging laundering methods to targeted updates in controls. Platforms can improve their systems further by analyzing data from internal audits, incident reports, and feedback from law enforcement. This information can then be used to retrain machine-learning models, adjusting thresholds for flagging suspicious transactions [5][6][7]. Tools like blockchain timestamping and digital watermarking can also confirm ownership and reduce counterfeit NFT activity [2][7]. Additionally, platforms might explore solutions like ScoreDetect for quick, automated takedown processes [3][7].
NFTs: The ultimate money laundering tool? – Maxim Kon, Cheksy
Conclusion
Tackling money laundering in NFTs requires a layered approach. No single measure – be it blockchain analytics, KYC procedures, or regulatory compliance – can fully address the risks posed by anonymity, cross-border transactions, resales, and price manipulation. U.S.-based NFT platforms need to implement comprehensive AML programs that integrate blockchain transparency to trace wallet histories and identify wash trading, identity verification to uncover high-risk users, transaction monitoring to detect unusual patterns, and adherence to FinCEN and Treasury guidelines.
Technology plays a critical role in strengthening these safeguards. Tools like digital watermarking and blockchain timestamping establish provenance and verify ownership, making it harder for criminals to exploit stolen or pirated content. Platforms such as ScoreDetect enhance protection by invisibly watermarking digital assets, tracking unauthorized copies, and using blockchain-backed checksums to minimize fraud. ScoreDetect’s automated delisting notices, with a 96% takedown success rate, ensure fraudulent listings are swiftly removed.
In addition to these technologies, adopting best practices – such as maintaining stolen-NFT registries and providing user education – helps sustain compliance and build trust. Platforms that prioritize risk-based compliance, transparent governance, and advanced monitoring tools not only strengthen their defenses but also gain credibility with users, regulators, and financial institutions. By combining blockchain analytics, robust KYC/EDD processes, regulatory alignment, and specialized technology, platforms can stay ahead of evolving criminal tactics while fostering innovation in the NFT space.
FAQs
How can NFTs be used for money laundering, and what are the common methods?
NFTs have opened up a new frontier for digital transactions, but they also come with risks, including their potential use in money laundering. Their decentralized nature and pseudonymous transactions make them appealing tools for hiding illicit activities.
One common tactic is wash trading, where an individual buys and sells the same NFT to artificially inflate its value, creating a false sense of demand. Another method involves using shell companies to obscure the true ownership of these digital assets. Additionally, NFTs can facilitate the transfer of funds across borders without much oversight, taking advantage of the limited transparency in certain NFT marketplaces and the inherent anonymity of blockchain technology.
How can money laundering in the NFT market be prevented?
Preventing money laundering in the NFT market calls for a mix of blockchain analytics, Know Your Customer (KYC) measures, and close cooperation with regulators.
By using blockchain analytics, platforms can monitor and trace transactions, helping to flag any unusual or suspicious behavior. KYC measures ensure user identities are verified, which limits the chances of anonymous or fraudulent activities. Additionally, partnering with regulatory bodies helps platforms align with anti-money laundering (AML) laws, creating a more secure and trustworthy digital space.
How do blockchain analytics and KYC protocols improve security on NFT platforms?
Blockchain analytics and KYC (Know Your Customer) protocols play a key role in boosting security on NFT platforms. By verifying user identities and maintaining transaction transparency, these tools help combat fraud, identify suspicious behavior, and minimize the chances of money laundering.
With blockchain analytics, platforms can monitor transaction histories and spot unusual activity. Meanwhile, KYC ensures that only verified, legitimate users are active in the marketplace. Together, these measures build a safer and more reliable space for NFT trading.

