Real-time audio watermarking is a cutting-edge solution to combat the growing problem of audio piracy. It embeds invisible, machine-readable identifiers directly into audio streams, ensuring ownership can be traced even after edits like compression, pitch shifts, or re-recording. This technology is particularly effective against modern piracy tactics and AI-generated manipulations like deepfakes.
Key Takeaways:
- Persistent Protection: Watermarks remain intact even after audio is shared, edited, or transformed.
- AI Integration: Advanced algorithms ensure watermarks survive distortions and modifications.
- Applications: Widely used in streaming platforms, digital cinema, corporate communications, and synthetic audio detection.
- Speed and Efficiency: Modern systems operate with latencies as low as three milliseconds, perfect for live audio.
Real-time watermarking outperforms traditional methods like DRM and audio fingerprinting by offering post-decryption security and resilience against common audio alterations. Tools like ScoreDetect further enhance this by combining watermarking with blockchain verification, making it easier to track and protect digital audio assets.
Responsible AI for Offline Plugins – Tamper-Resistant Neural Audio Watermarking – Kanru Hua ADC 2024
How Real-Time Audio Watermarking Works
When it comes to safeguarding digital audio, real-time watermarking needs to strike a delicate balance: it must be inaudible to listeners but strong enough to withstand various audio alterations. This process embeds a unique digital identifier directly into an audio stream in real time. The clever part? The watermark blends seamlessly into the audio, making it undetectable to the human ear while remaining identifiable by specialized software.
Embedding and Detecting Watermarks
The embedding process relies on techniques like spread-spectrum methods and psychoacoustic masking. Spread-spectrum disperses the watermark’s energy across a broad range, while psychoacoustic masking takes advantage of how humans perceive sound. By tweaking the audio based on its volume, the watermark stays hidden. Additionally, this method adjusts only the magnitude of the Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) while keeping the original phase intact, ensuring the audio quality remains natural [7].
On the detection side, most systems use blind extraction, meaning they can identify the watermark without needing the original audio file. In fact, about 90% of modern systems operate this way [4]. Technological advancements have made detection incredibly efficient, with single-pass detectors working up to 100 times faster than older models [1]. Some frameworks can encode 32 bits per second while maintaining latency under three milliseconds [2][3].
Now let’s dive into how these watermarks hold up under audio modifications.
Resisting Audio Alterations
For a watermark to be effective, it must survive common audio edits like MP3 compression, added noise, or filtering. Enter Invertible Neural Networks (INN), which process both audio and watermark data simultaneously. This ensures the watermark can still be retrieved even after the audio has been altered [9][10]. Another tool, the Bitwise Readout Head, aggregates data over time, enabling reliable decoding even when the audio has been cut, reordered, or desynchronized [7].
When dealing with time-scale changes – like stretching or shrinking audio – Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) steps in to maintain the watermark’s traceability [5]. Some systems have demonstrated impressive resilience, achieving an Area Under the Curve (AUC) score of 0.957 across over 20 different audio transformations [5]. Others have reduced Bit Error Rates (BER) by more than 2,800% compared to older methods [3]. In fact, some implementations boast near-perfect detection even under extreme environmental and signal variations [8].
Building on these advancements, AI has taken watermarking to the next level.
The Role of AI and Advanced Algorithms
Artificial intelligence has revolutionized watermarking by making it even more robust. For instance, advanced systems now use adversarial optimization in the time-frequency domain to create "edit-aware" watermarks. These watermarks adapt to distortions without relying on pre-set attack scenarios [7]. As researchers Li et al. explain:
Watermarking optimizes signal perturbations to guide detector outputs. [7]
Key-controllable frameworks add another layer of security by incorporating cryptographic keys. Only users with the correct key can decode the watermark. These systems also replace traditional random sampling with Predict Modules, which use features specific to the audio for better decoding accuracy [9]. Plus, their consistent computational efficiency makes them ideal for low-power devices like Bluetooth headsets [8].
Where Real-Time Audio Watermarking Is Used
Real-time audio watermarking has become a critical tool in industries where protecting content is a top priority. From combating piracy in entertainment to safeguarding corporate communications, this technology addresses gaps that older security measures can’t fill. Here’s a closer look at its applications.
Media and Entertainment Industry
The media world constantly battles piracy, and real-time watermarking has emerged as a powerful defense. Streaming platforms now rely on this technology to identify illegal recordings and take action swiftly [8].
In digital cinema, a method called "traitor tracing" embeds unique projector IDs and timestamps into soundtracks during playback [11]. This allows authorities to trace pirated recordings back to their source. Technologies like Cinavia add another layer of protection by muting or stopping playback of unauthorized copies on consumer devices [11].
Live streaming, with its rapid content distribution, poses unique challenges. Systems equipped with "takedown gates" now monitor uploads in real time, blocking pirated material before it reaches viewers [5]. For example, Amazon’s watermarking algorithm can detect unauthorized recordings using just two seconds of audio, even when recorded from over 20 feet away [8]. Yuan-Yen Tai, a Research Scientist at Amazon, explains:
Audio content that Alexa plays – music, audiobooks, podcasts, radio broadcasts, movies – could be watermarked on the fly, so that Alexa-enabled devices can better gauge room reverberation and filter out echoes. [8]
This technology also helps smart devices avoid accidental wake-ups caused by media mentions, like an ad saying "Alexa" [8].
Beyond public media, similar techniques are used to secure private communications.
Business and Corporate Applications
While media platforms fight piracy, businesses face the challenge of protecting sensitive internal communications. Real-time watermarking helps by embedding unique identifiers, such as timestamps and user IDs, into audio streams during live meetings [11]. These watermarks remain intact even after decryption, ensuring end-to-end security [2][4]. With latency as low as 3 milliseconds, this technology is perfect for video calls and conferences where delays could disrupt the flow [2].
Additionally, companies can watermark proprietary audio assets with machine-readable copyright markers, preventing unauthorized use by AI models. Under Section 1202 of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), these watermarked assets are legally protected, allowing companies to take action against those who remove or tamper with the embedded information [6].
This approach also helps counter threats from synthetic audio and deepfakes.
Synthetic Audio and Deepfake Detection
The rise of AI-generated voices has introduced new risks, including fraud and misinformation. In one instance, scammers used a voice deepfake to impersonate a CEO and trick an employee into transferring $243,000 to a fraudulent account [12]. Real-time watermarking offers a way to verify the authenticity of audio by embedding identifiers that confirm its origin [1][3].
Tools like AudioSeal are designed to detect synthetic segments within a larger audio file. This is particularly useful for identifying altered deepfakes where only specific words or phrases have been manipulated [1]. Robin San Roman, the lead author of AudioSeal research, highlights:
AudioSeal is the first audio watermarking technique designed specifically for localized detection of AI-generated speech. [1]
The technology enables platforms to spot manipulated content quickly, with detection speeds far outpacing older models [1]. Watermarking can be applied at two levels:
- Model-level watermarking, which integrates into AI systems to automatically label synthetic outputs.
- User-level watermarking, which protects original audio before sharing. If this audio is later scraped for AI training, the watermark carries over, making it easier to track intellectual property [12].
Guangyu Chen, a researcher in this field, emphasizes:
Watermarking presents a proactive and robust defence mechanism against these looming risks [voice fraud and speaker impersonation]. [3]
These advancements are a crucial step toward stronger media and content protection.
| Application | Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Live Streaming | Takedown Gates | Prevents piracy in real time during uploads |
| Digital Cinema | Traitor Tracing | Tracks the source of unauthorized recordings |
| Smart Speakers | Second-Screen Sync | Avoids accidental activation from media ads |
| Music Platforms | Royalty Monitoring | Tracks ownership and ensures accurate payouts |
| Podcasting | UGC Vetting | Identifies duplicate or pirated content |
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Benefits and Drawbacks of Real-Time Audio Watermarking
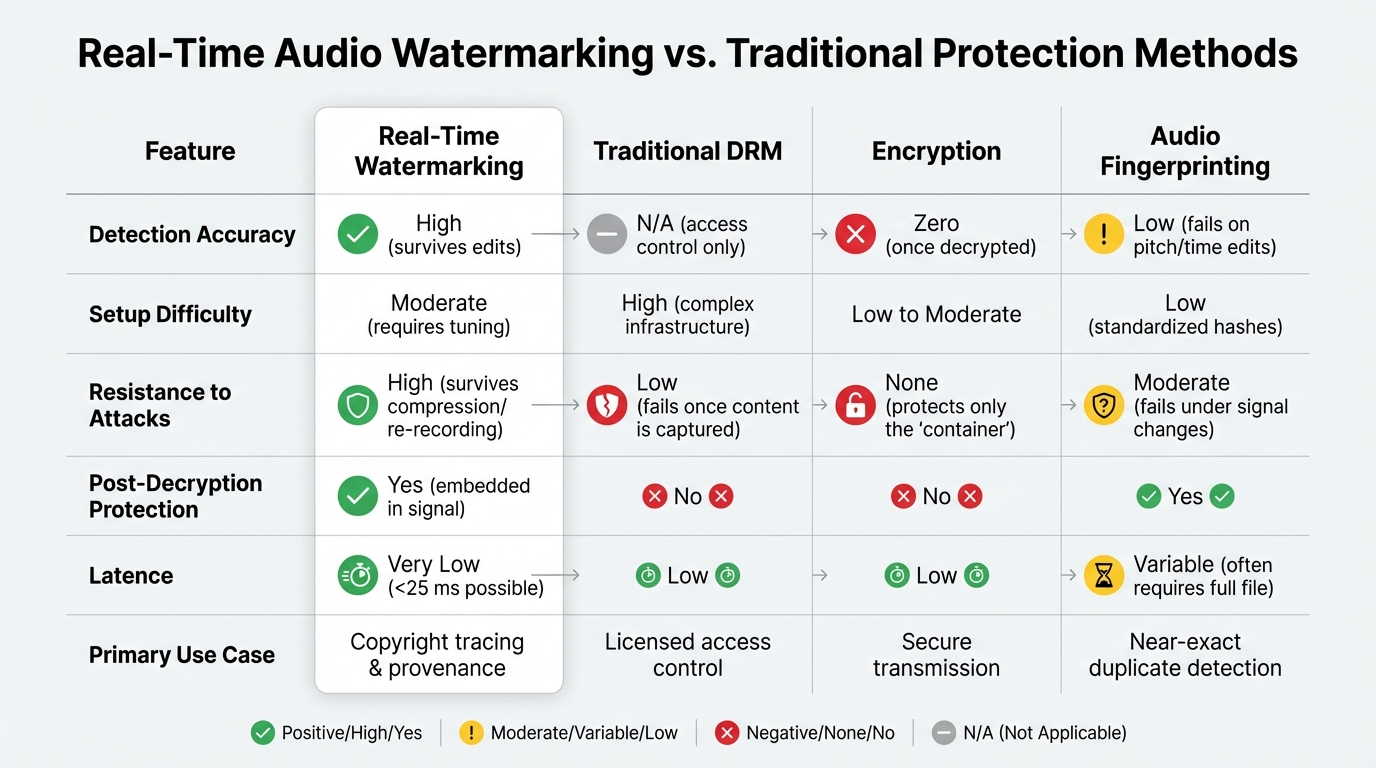
Real-Time Audio Watermarking vs Traditional Protection Methods Comparison
Real-time audio watermarking offers a robust way to protect digital audio, but it comes with its own set of trade-offs. Let’s break down the key advantages, the challenges it faces, and how it stacks up against older methods.
Main Benefits of Real-Time Watermarking
One major advantage of watermarking is its persistence. Unlike encryption, which only protects content until it’s accessed, watermarks remain embedded in the audio even after it’s shared or copied. This makes it possible to trace leaked files back to their source, even if metadata has been stripped away [4].
Watermarking systems are also highly resilient. They can withstand common signal processing alterations like MP3 compression, pitch shifts, time stretching, and equalization – edits that often defeat older fingerprinting methods [5]. For example, the HashWave framework demonstrated a detection accuracy of 95.7% (AUC of 0.957) across 20 different signal-processing transformations [5].
Speed is another strong point. Modern detectors are up to 100 times faster than older models, with some achieving latencies as low as three milliseconds [1][2]. For live applications, advanced spread spectrum techniques can keep delays under the 25-millisecond threshold needed for interactive performances [2].
Additionally, advanced watermarking systems offer precise tamper detection. Instead of flagging an entire file, they can identify the exact segments that have been altered or synthetically modified. This level of detail goes far beyond what traditional file-level DRM can provide [1].
Problems and Limitations
Despite its strengths, real-time audio watermarking comes with challenges. One of the biggest hurdles is balancing imperceptibility, capacity, and robustness. Improving one of these factors often comes at the expense of another [2].
Transform-domain systems, which embed watermarks by manipulating audio frequency or time domains, require significant computational power – especially for lengthy audio files. However, parallel processing across multiple CPU cores can cut execution times by as much as 70% to 90% [13].
Latency is another concern, especially for real-time applications. While smaller buffer sizes (e.g., 256 samples) can reduce delays, this often compromises embedding capacity and psychoacoustic masking accuracy [2]. For example, networked music performances demand latencies under 25 milliseconds to maintain timing and interaction [2].
Desynchronization also poses a threat. Edits like cropping, splicing, or temporal cuts can disrupt the watermark’s structure, making it difficult to retrieve the embedded message. Although newer systems, such as AWARE, are designed to handle these challenges, they are not entirely immune [7].
Finally, sophisticated removal techniques represent a significant risk. Adversaries using non-linear distortions or adversarial methods can sometimes strip watermarks while maintaining the audio’s perceptual quality [5].
Comparison Table: Real-Time Watermarking vs. Older Methods
Here’s a side-by-side look at how real-time watermarking compares to other approaches:
| Feature | Real-Time Watermarking | Traditional DRM | Encryption | Audio Fingerprinting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detection Accuracy | High (survives edits) | N/A (access control only) | Zero (once decrypted) | Low (fails on pitch/time edits) |
| Setup Difficulty | Moderate (requires tuning) | High (complex infrastructure) | Low to Moderate | Low (standardized hashes) |
| Resistance to Attacks | High (survives compression/re-recording) | Low (fails once content is captured) | None (protects only the "container") | Moderate (fails under signal changes) |
| Post-Decryption Protection | Yes (embedded in signal) | No | No | Yes |
| Latency | Very Low (<25 ms possible) | Low | Low | Variable (often requires full file) |
| Primary Use Case | Copyright tracing & provenance | Licensed access control | Secure transmission | Near-exact duplicate detection |
Real-time watermarking stands out for its ability to provide post-decryption protection and its resilience against common signal edits. However, it does require more advanced setup compared to simpler methods like encryption or fingerprinting. This combination of strengths and challenges highlights its growing importance in the field of media protection.
ScoreDetect: A Complete Tool for Audio Watermarking and Media Protection
ScoreDetect takes media protection to the next level by combining watermarking, detection, and enforcement into one seamless system.
Stopping Piracy with Watermarking
ScoreDetect uses psychoacoustic models to embed watermarks below the audible range, ensuring ownership data is permanently integrated into the audio signal[2][4][6]. This process works in real time, with minimal delay (just 256-512 sample buffers), achieving sub-3 millisecond latency for live streams[2]. Even with this speed, the watermarks maintain excellent speech clarity, as shown by high scores on PESQ and STOI tests[7]. By offering a fast and reliable way to protect audio, ScoreDetect meets the demands of today’s fast-paced media environment.
Find, Review, and Remove Stolen Content
ScoreDetect doesn’t just prevent piracy – it actively tracks down unauthorized copies of audio online. Its smart web scraping technology bypasses detection barriers 95% of the time, identifying pirated content with impressive accuracy. Once located, ScoreDetect analyzes altered segments and issues automated takedown requests, achieving a 96% success rate in removing stolen material.
Blockchain Technology for Copyright Protection
To strengthen copyright protection, ScoreDetect leverages blockchain technology by registering audio fingerprints on the Ethereum blockchain through smart contracts. This creates a tamper-proof record of ownership[5]. Instead of storing full audio files, the system records a checksum and metadata using the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS)[5]. This decentralized setup ensures content can be verified without depending on a central authority.
Blockchain integration also allows creators to prove ownership, even if the audio has been altered or re-encoded[5]. For WordPress users, ScoreDetect offers a plugin that automatically logs every published or updated article on the blockchain, providing verified proof of ownership. Plus, this feature aligns with Google’s E-E-A-T standards, enhancing SEO performance. By combining blockchain verification with advanced watermarking, ScoreDetect sets a new standard for digital copyright protection.
Conclusion: Protecting Digital Audio Content
As media piracy continues to evolve, traditional protective measures are proving inadequate. Real-time audio watermarking offers a solution by embedding invisible, permanent ownership markers that endure file transformations, compression, and even manipulation by AI. According to C. Jair Santin-Cruz and G. Jovanovic Dolecek from the National Institute of Astrophysics, Optics and Electronics:
The increasing prevalence of audio sharing through real-time streams or video calls is a pressing issue requiring low-latency systems [2].
This shift in the digital landscape calls for a proactive approach. Live content, AI-generated audio, and decentralized distribution models demand tools that can actively defend intellectual property. Around 90% of modern audio watermarking algorithms are "blind" systems, meaning they don’t need the original file to verify ownership [4]. This capability allows businesses to monitor and secure content across multiple platforms. Additionally, these systems provide legal protection under Section 1202 of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), empowering creators to combat piracy [6].
Tools like ScoreDetect combine real-time watermarking with intelligent detection, automated takedown mechanisms, and blockchain verification to offer a robust defense. For businesses managing audio assets – whether podcasts, music, corporate communications, or educational material – this level of protection is increasingly essential.
Microsoft Research underscores the importance of watermarking as a defense against voice fraud and speaker impersonation [3]. By adopting solutions like ScoreDetect, organizations can not only protect their assets but also maintain a competitive edge in today’s digital-first world.
Safeguarding digital audio content requires more than reactive measures. It demands systems that operate in real time, withstand manipulation, and provide undeniable proof of ownership. Advanced watermarking technology ensures your audio assets remain secure and protected from emerging threats.
FAQs
What makes real-time audio watermarking different from traditional DRM methods?
Real-time audio watermarking takes a different approach compared to traditional DRM methods by embedding inaudible identifiers directly into the audio during playback or streaming. These identifiers allow content to be tracked and monitored instantly, even in live environments, without interrupting the listener’s experience.
Traditional DRM often relies on encryption or access controls, which can sometimes be bypassed. In contrast, real-time audio watermarking embeds a unique, invisible "fingerprint" within the audio itself. This makes continuous monitoring possible and enables quick responses to piracy, such as initiating takedowns or pursuing legal actions. It’s particularly effective for live broadcasts or streaming, where traditional DRM methods may fall short in providing immediate protection.
By offering real-time detection and seamless integration, audio watermarking provides a more flexible and effective way to safeguard digital media.
What challenges arise when implementing real-time audio watermarking?
Implementing real-time audio watermarking isn’t without its challenges. One of the biggest obstacles is making sure the watermark can withstand distortions like compression, background noise, reverberation, and various signal processing methods. These elements have the potential to weaken or even erase the watermark, making it harder to detect later. At the same time, the watermark needs to be invisible to listeners to preserve the audio’s quality. This creates a tricky balancing act between durability and subtlety.
Another issue is protecting the watermark from intentional tampering. Techniques like time stretching, polarity inversion, or signal manipulation can interfere with the watermark’s integrity. On top of that, real-time processing adds another layer of complexity. To work effectively, the algorithms must deliver low latency, meaning they have to process audio quickly and accurately without introducing delays. Maintaining this level of performance while keeping the audio quality intact is no small feat.
How does AI improve the effectiveness of real-time audio watermarking?
AI is transforming real-time audio watermarking by making it stronger, more secure, and better equipped to handle challenges. With advanced algorithms, AI embeds watermarks that can withstand edits, distortions, or tampering, all while preserving the original audio quality. These techniques ensure that the watermarks stay invisible to listeners but can be identified when necessary.
AI-driven systems go a step further by simulating potential threats, like signal processing or re-encoding, to fine-tune watermark placement and boost their durability. On top of that, machine learning models continually refine detection methods, allowing precise identification even after the audio undergoes multiple changes. This blend of precision and adaptability makes AI an essential tool for safeguarding digital media from piracy.

