Consensus algorithms are the backbone of blockchain technology, ensuring secure, decentralized systems without a central authority. For copyright data, these algorithms enable tamper-proof records, efficient rights management, and transparent ownership tracking. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Proof of Work (PoW): High security but energy-intensive; suited for archiving original works.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Energy-efficient with moderate speed; ideal for digital rights marketplaces.
- Proof of Authority (PoA): Fast and low-cost; works best for private networks with trusted validators.
- K-Raft Algorithm: Specialized for image copyright, offering faster processing and stronger watermark protection.
Blockchain platforms like ScoreDetect use these methods to timestamp content, embed invisible watermarks, and automate copyright workflows, achieving high success rates in content protection and takedown actions. These technologies simplify copyright management, reduce costs, and improve reliability.
All Major Blockchain Consensus Algorithms Explained | Consensus Mechanism in Blockchain
sbb-itb-738ac1e
Main Consensus Algorithms for Copyright Protection
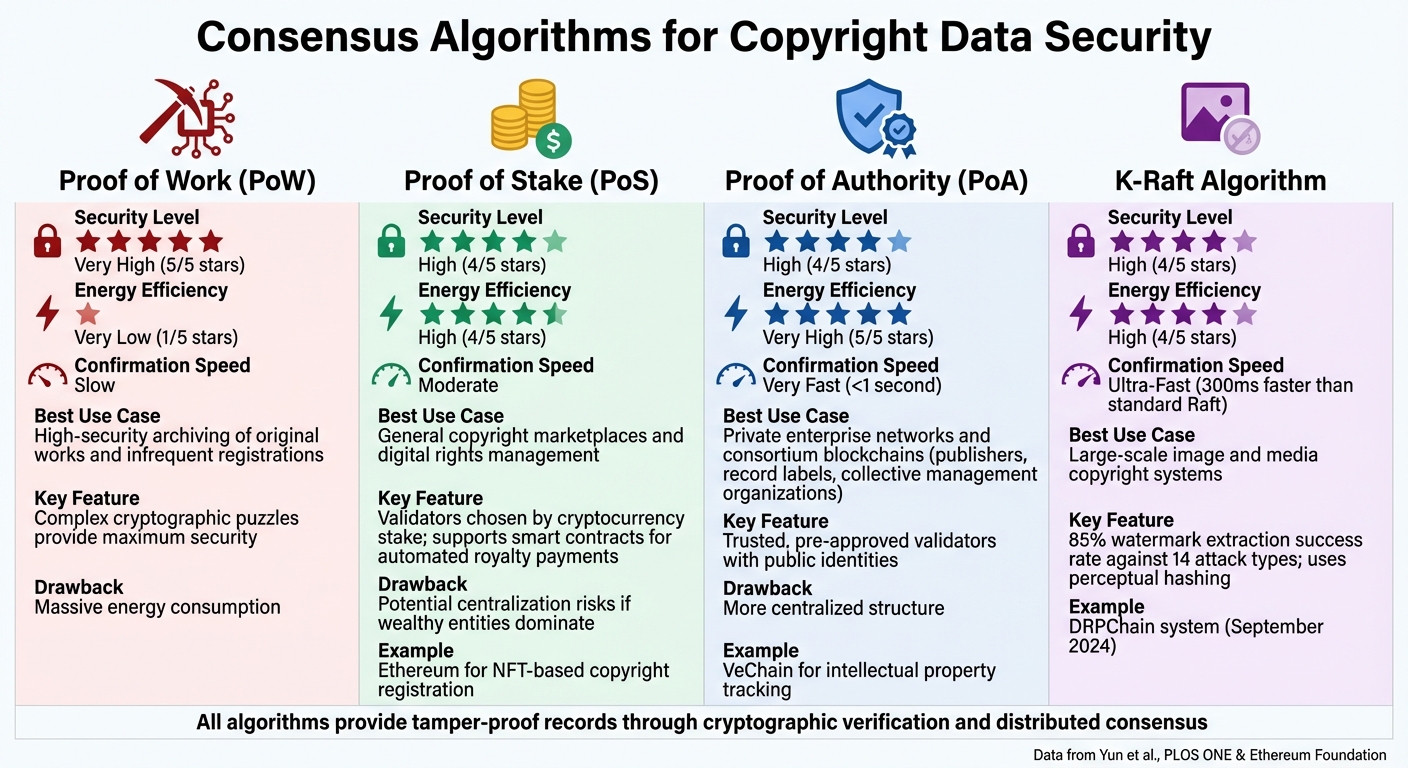
Comparison of Blockchain Consensus Algorithms for Copyright Protection
Proof of Work (PoW) for Copyright Verification
Proof of Work (PoW) operates by requiring nodes to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. When applied to copyright protection, this mechanism offers a very high level of security, particularly for verifying the authenticity of original content [4]. However, PoW comes with significant downsides – it consumes a massive amount of energy and operates at a slower pace. These limitations make it better suited for securely archiving original works rather than handling the high volume of copyright claims that might arise daily.
"PoW provides high security but consumes vast energy. At the same time, PoS and its variant DPoS are more efficient and consume less energy, although they may introduce centralization risks." – Yun et al., PLOS ONE [4]
For those seeking a more energy-conscious solution, Proof of Stake (PoS) offers an attractive alternative.
Proof of Stake (PoS) for Energy-Efficient Protection
Proof of Stake (PoS) takes a different approach by eliminating energy-intensive mining. Instead, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they’ve staked. This makes PoS far more energy-efficient while still maintaining strong security [4]. Ethereum’s transition to PoS is a prime example, as it has become a popular platform for digital rights management and NFT-based copyright registration. Its support for smart contracts enables automated royalty payments, further enhancing its appeal [2].
However, PoS isn’t without its challenges. One of the main concerns is centralization – if a small number of wealthy entities control most of the stake, they could dominate the validation process, which could undermine the system’s fairness [4].
Building on these ideas, Proof of Authority (PoA) offers another layer of efficiency, leveraging trusted validators for copyright management.
Proof of Authority (PoA) for Trusted Copyright Networks
Proof of Authority (PoA) relies on the reputation and identity of validators rather than computational power or financial stakes. In this system, a limited group of pre-approved, trusted entities serve as validators [1].
"Proof-of-authority is a reputation-based consensus algorithm that requires trusting a set of authorized signers to produce blocks, instead of a stake-based mechanism in PoS." – Ethereum Foundation [1]
PoA is particularly effective for private or consortium blockchains, where groups like publishers, record labels, or collective management organizations manage a shared copyright ledger. This approach offers both speed and security, with transaction confirmation times as fast as under one second due to the limited number of trusted nodes involved [1]. For instance, VeChain employs a modified PoA model to track intellectual property and supply chain data efficiently. To prevent censorship, the protocol limits each signer to minting only one out of every N/2 blocks [1]. While PoA’s structure is more centralized, its speed and low operational costs make it a practical choice for organizations with established trust networks.
Innovative adaptations of these systems continue to emerge. A standout example is DRPChain, a blockchain tailored for copyright protection.
In September 2024, a research team led by Professor Jian Yun introduced DRPChain, a blockchain system specifically designed for image copyright protection. DRPChain uses a specialized K-Raft algorithm, which improves efficiency by 300 milliseconds compared to the standard Raft algorithm and achieves an 85% success rate in watermark extraction against 14 different image attacks. The system employs perceptual hashing to select leader nodes based on Hamming distance, showcasing how consensus methods can be customized for precise copyright needs [4].
Benefits of Consensus Algorithms for Copyright Data
Preventing Data Tampering
Consensus algorithms provide a strong safeguard against tampering with copyright records by requiring agreement from multiple nodes before any data can be added to the blockchain. Each block is cryptographically tied to the one before it using hash pointers and timestamps. This structure makes altering a single record practically impossible. In Proof of Work (PoW) systems, the computational effort required to recalculate every subsequent block acts as a deterrent, while in Proof of Authority (PoA) networks, where validator identities are public, tampering would severely damage the validator’s reputation [3].
In PoA systems, only pre-approved entities can validate blocks. If a validator acts maliciously, their identity is exposed, allowing the network to remove them through a vote [1].
For example, the K-Raft algorithm used by DRPChain enhances tamper-resistance by reducing errors and improving watermark extraction [4].
This tamper-proof structure not only protects the integrity of copyright data but also promotes a unified and transparent system for managing intellectual property.
Improving Transparency and Trust
Traditional copyright systems often operate in silos, with ownership details scattered across private databases managed by publishers, record labels, and rights organizations. Consensus-based blockchains address this problem by creating a shared, single source of truth that all stakeholders can access. This eliminates the need for centralized intermediaries, which can fail or create disputes.
The collapse of the Global Repertoire Database (GRD) highlights the dangers of fragmented systems. Consensus algorithms help avoid such failures by automatically detecting conflicting claims – such as two parties claiming the same share of a song – and resolving them transparently.
One practical example comes from August 2020, when researchers used a permissioned blockchain on the Alastria Network to manage musical rights for Collective Management Organizations. Using Istanbul Byzantine Fault Tolerance (IBFT) consensus, the system deployed smart contracts to identify and resolve overlapping claims in real-time [5].
Scalability and Efficiency
In addition to enhancing security and transparency, consensus algorithms significantly boost scalability and operational efficiency. Each algorithm offers unique advantages depending on the use case. For instance, Proof of Authority (PoA) can confirm transactions in under one second by restricting validation to a small, trusted group of signers, reducing network communication delays [1].
The K-Raft algorithm, designed for image copyright management, improves processing speed by 300 milliseconds compared to standard Raft and delivers better throughput than both PoW and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) [4].
| Consensus Algorithm | Confirmation Speed | Energy Efficiency | Best Copyright Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proof of Work (PoW) | Slow | Very Low | High-security, infrequent registrations |
| Proof of Stake (PoS) | Moderate | High | General copyright marketplaces |
| Proof of Authority (PoA) | Very Fast (<1s) | Very High | Private enterprise networks [1] |
| K-Raft | Ultra-Fast | High | Large-scale image/media systems [4] |
To further enhance efficiency, many systems store metadata on the blockchain while linking to off-chain distributed storage for the actual media files. This approach prevents blockchain bloat while retaining the security benefits [2][4]. These improvements in scalability and efficiency pave the way for advanced copyright management solutions.
How ScoreDetect Uses Consensus Algorithms
Blockchain Timestamping with ScoreDetect
ScoreDetect offers a simple yet powerful way to establish proof of ownership for your digital content. By generating a cryptographic checksum of your files and recording it on the blockchain, the platform ensures your copyright records are secure and unchangeable. Each block in the chain links to the one before it using hash pointers, making it nearly impossible to alter these records once they’re created.
Here’s how it works: ScoreDetect creates a unique SHA-256 hash for your content and stores it on the blockchain. Even the slightest modification to the original file will generate an entirely different hash, making tampering immediately obvious. This blockchain-based validation eliminates the need for traditional copyright offices, which can be both expensive and time-consuming.
For WordPress users, ScoreDetect’s plugin adds another layer of convenience. It automatically captures every article you publish or update, generating blockchain-verified certificates in around 3 seconds. This speed is thanks to efficient consensus mechanisms, similar to Proof of Authority (PoA) systems, where trusted validators ensure transactions are processed in under a second. On top of that, the plugin boosts your SEO by showcasing your content’s authenticity to search engines through Google’s E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness).
Invisible Watermarking and Detection
For those looking for even stronger protection, ScoreDetect’s Enterprise plan combines blockchain technology with invisible watermarking. These watermarks are subtle, non-intrusive, and embedded into various types of content, including images, videos, audio, and documents. They carry perceptual hashes, which stay intact even if the content is resized, compressed, or cropped.
Unlike traditional cryptographic hashes, perceptual hashes are designed to recognize content even after minor edits. This makes them invaluable for tracking unauthorized use across the web. The platform records these perceptual hashes on the blockchain, creating a permanent reference point for your content. ScoreDetect’s detection system is highly effective, with a 95% success rate in bypassing web scraping prevention measures. This means it can reliably locate your protected content on platforms worldwide.
When unauthorized use is found, the platform’s tools compare the discovered content to the blockchain record, providing quantitative proof. This process generates undeniable evidence for copyright disputes, leveraging the same cryptographic principles that secure financial systems. These advanced methods streamline copyright management and make enforcement both efficient and reliable.
Automated Workflows for Copyright Management
ScoreDetect takes things further by automating copyright management with workflows powered by blockchain consensus. Through integration with over 6,000 web applications via Zapier, the platform enables automated actions like takedowns or registry updates based on blockchain-validated data. These workflows eliminate the need for manual intervention, saving time and effort.
The platform’s takedown system is particularly effective, achieving a 96% success rate in removing unauthorized content. This success is largely due to the irrefutable proof provided by blockchain timestamps, which establish clear ownership and precedence. When you file a delisting notice, the blockchain record acts as cryptographic evidence that cannot be disputed or altered.
For enterprise clients, ScoreDetect offers continuous monitoring and automated responses powered by smart contracts. These contracts use blockchain-validated data to trigger real-time actions, ensuring your digital assets are protected 24/7 without the need for human oversight. This system provides a seamless way to track and manage content globally, overcoming the limitations of traditional copyright enforcement that often struggles with geographical boundaries.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
Consensus algorithms play a central role in securing blockchain-based copyright solutions. By enabling secure, direct connections across distributed networks, they eliminate the need for costly third-party verification systems [6]. These algorithms create a single, tamper-resistant ledger, safeguarded through cryptographic verification. Using Merkle trees, even the slightest data alteration generates a completely different hash, making tampering instantly noticeable [2]. These principles form the backbone of how ScoreDetect applies blockchain technology to protect intellectual property in practical scenarios.
ScoreDetect’s Role in Copyright Protection
ScoreDetect showcases the potential of blockchain and consensus algorithms in managing digital copyright. The platform generates cryptographically secured certificates, creating unchangeable records of ownership without relying on traditional copyright offices. Its Enterprise plan enhances this with blockchain validation and invisible watermarking, achieving a 95% success rate in bypassing web scraping defenses. Additionally, its automated takedown system successfully removes unauthorized content 96% of the time. These achievements are made possible by blockchain-based timestamps, which provide clear proof of ownership and precedence.
Future of Blockchain Copyright Systems
Looking ahead, blockchain copyright systems are expected to integrate more advanced consensus mechanisms and hybrid designs. For example, research on DRPChain published in September 2024 demonstrated that the K-Raft consensus algorithm improved watermark extraction success rates by 10% and reduced block generation errors by 2% [4]. The industry is also shifting toward more efficient models like Proof of Stake and Delegated Proof of Stake, which address challenges like scalability and energy consumption [7]. Future systems will likely combine on-chain validation with off-chain storage solutions, such as IPFS, where cryptographic fingerprints are stored on the blockchain while full media files remain external.
"Blockchain technology is an ideal choice for recording transaction history and addressing content privacy and security concerns." – Professor Jian Yun [4]
With over 25 countries investing in blockchain technology and more than $1.3 billion allocated to its development as of 2020 [3], consensus-based copyright systems are well-positioned to become the global standard for protecting digital assets.
FAQs
How do consensus algorithms protect copyright data on the blockchain?
Consensus algorithms are at the heart of securing copyright data within blockchain systems. Algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) ensure that transactions – such as registering a content checksum – are validated by a majority of participants in the network before being added to the blockchain. This validation process guarantees that the data becomes unchangeable (immutable), meaning it can’t be altered without disrupting the entire chain. It also provides fault tolerance, allowing the system to keep functioning even if some nodes fail or behave maliciously.
In the context of copyright protection, these algorithms turn a content checksum into a tamper-proof proof of ownership. Once verified and added to the blockchain, the checksum is replicated across multiple independent nodes. This decentralized setup prevents any single party from modifying ownership claims or timestamps. The result? Enhanced transparency that bolsters copyright enforcement and ensures ownership records are verifiable on a global scale. ScoreDetect applies this technology to securely record content checksums, delivering a dependable solution for safeguarding digital assets.
What are the key differences between Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, and Proof of Authority in managing copyright data?
Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Proof of Authority (PoA) are three distinct methods used to secure copyright data. Each has its own strengths, weaknesses, and ideal applications.
PoW is based on solving intricate computational puzzles. This makes it extremely secure and resistant to tampering. However, it comes with significant downsides: high energy consumption and slower transaction speeds. These limitations can make it less practical for systems that need frequent updates or handle large volumes of content.
PoS takes a different approach by relying on validators who lock up cryptocurrency as a "stake" to propose and validate blocks. This method is much more energy-efficient and processes transactions faster, making it a better fit for systems that require regular copyright timestamping. That said, its security hinges on how evenly stakes are distributed – if a few parties hold most of the stake, they could exert undue influence.
PoA, on the other hand, relies on a select group of trusted authorities to validate transactions. This method is incredibly fast and uses minimal energy, making it an excellent choice for private copyright systems operated by known entities, such as publishers or rights organizations. The downside? It sacrifices decentralization, as the system’s integrity depends entirely on the honesty of these trusted authorities.
Each method has its place: PoW ensures maximum security at a high cost, PoS strikes a balance between efficiency and decentralization, and PoA offers speed and simplicity for trusted, private systems.
What role does the K-Raft algorithm play in protecting image copyrights?
The Raft consensus algorithm plays a key role in blockchain systems like Hyperledger Fabric. It’s designed to create tamper-resistant and sequential records of transactions, which can include those tied to image ownership. However, there doesn’t appear to be any detailed information about a "K-Raft" variant or how it might specifically improve the protection of image copyrights. Without more context, it’s challenging to identify any unique benefits it could provide for safeguarding image copyrights.

