Neural network audio watermarking is reshaping how audio content is protected. By embedding hidden data into sound, these systems ensure it remains intact even after compression, noise, or edits. Tools like AWARE, WavMark, and SyncGuard demonstrate how this technology balances sound quality and data durability. Key results include:
- AWARE: Achieves a low error rate (1.61%) under neural vocoder processing with high-quality audio metrics (PESQ 4.08, STOI 0.97).
- WavMark: Encodes 32 bits per second with an average error rate of 0.48% across 10 attack scenarios.
- SyncGuard: Maintains 97.72% accuracy under time-scale changes and achieves superior audio quality (SNR 28.27 dB).
These methods also support tracing audio origins, safeguarding against misuse, and ensuring ownership proof through blockchain integration. With rising AI-driven threats, neural watermarking offers a reliable way to protect and verify audio content.
Responsible AI for Offline Plugins – Tamper-Resistant Neural Audio Watermarking – Kanru Hua ADC 2024
Real-World Applications: Case Studies
These case studies showcase the practical benefits of neural network watermarking in safeguarding audio content.
Case Study 1: Encoder-Decoder Networks for Audio Protection
In October 2025, researcher Kosta Pavlović and his team introduced AWARE (Audio Watermarking via Adversarial Resistance to Edits), an encoder-decoder system designed to endure even the most aggressive audio edits. By employing adversarial optimization in the time-frequency domain, they developed watermarks capable of remaining detectable after significant manipulation [1].
AWARE’s design incorporates a Bitwise Readout Head (BRH), which consolidates temporal evidence into per-bit scores. This feature proved essential during tests against the BigVGAN neural vocoder, a high-fidelity voice cloning tool. Even under neural vocoder resynthesis, AWARE achieved a remarkably low Bit Error Rate (BER) of just 1.61%, outperforming other methods by a wide margin [1].
The system didn’t compromise audio quality either, achieving a PESQ score of 4.08 and a STOI of 0.97, while embedding 16 bits per second. Even in tough conditions like band-stop filtering, AWARE recorded an impressive BER of only 0.95% [1]. These results highlight its ability to balance imperceptibility and robustness – two key elements of effective watermarking.
"The target is not a semantic entity localized in space or time. It is a weak, distributed pattern, encoding bits that must be sequence-consistent under time-warping and cutting", Pavlović explained [1].
With AWARE’s success, the focus shifts to watermarking solutions for protecting AI training datasets.
Case Study 2: Watermarking AI Training Datasets
In January 2024, Guangyu Chen and his team at Microsoft Research Asia introduced WavMark, a framework aimed at safeguarding audio datasets from unauthorized use in AI training. WavMark embeds 32 bits of data into 1-second audio segments, offering a robust defense against voice fraud and speaker impersonation [3].
During testing on 10- to 20-second audio clips, WavMark achieved an average BER of just 0.48% across various attack scenarios, representing a 2,800% improvement over earlier methods [3]. Its resilience extends to generative AI processes: when watermarked audio is used for training, the watermark is preserved in the AI-generated output, making provenance tracking possible. This enables creators to protect their intellectual property without relying on broader, industry-wide watermarking standards [4].
"Unlike the conventional approach of solely relying on passive methods for detecting synthetic data, watermarking presents a proactive and robust defence mechanism against these looming risks", Chen stated [3].
The final case study explores dual-embedding strategies that enhance speed and accuracy in watermarking.
Case Study 3: Embedding Functional Data in Audio
In September 2024, researchers Pengcheng Li and Xulong Zhang from Ping An Technology (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. developed IDEAW (Invertible Dual-Embedding Audio Watermarking) to streamline watermark extraction from large datasets. IDEAW employs a two-stage Invertible Neural Network (INN), allowing a lightweight "locating code" to be embedded separately from the full watermark message. This enables quick scanning before extracting the full message [2].
In August 2025, Zhenliang Gan and his team at Fudan University introduced SyncGuard, a system designed to resist temporal distortions. SyncGuard uses a frame-wise broadcast embedding strategy, embedding the complete watermark into every audio frame feature. This eliminates the need for localization and enhances efficiency. SyncGuard achieved a Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) of 28.27 dB, outperforming traditional methods like FSVC (24.23 dB) and FDLM (25.83 dB), while maintaining a PESQ score of 4.02 [5].
"The frame-wise embedding strategy eliminates the need to address the localization problem", Gan noted [5].
These case studies underscore how neural network watermarking is advancing the protection of audio content across diverse applications.
Comparing Results Across Case Studies
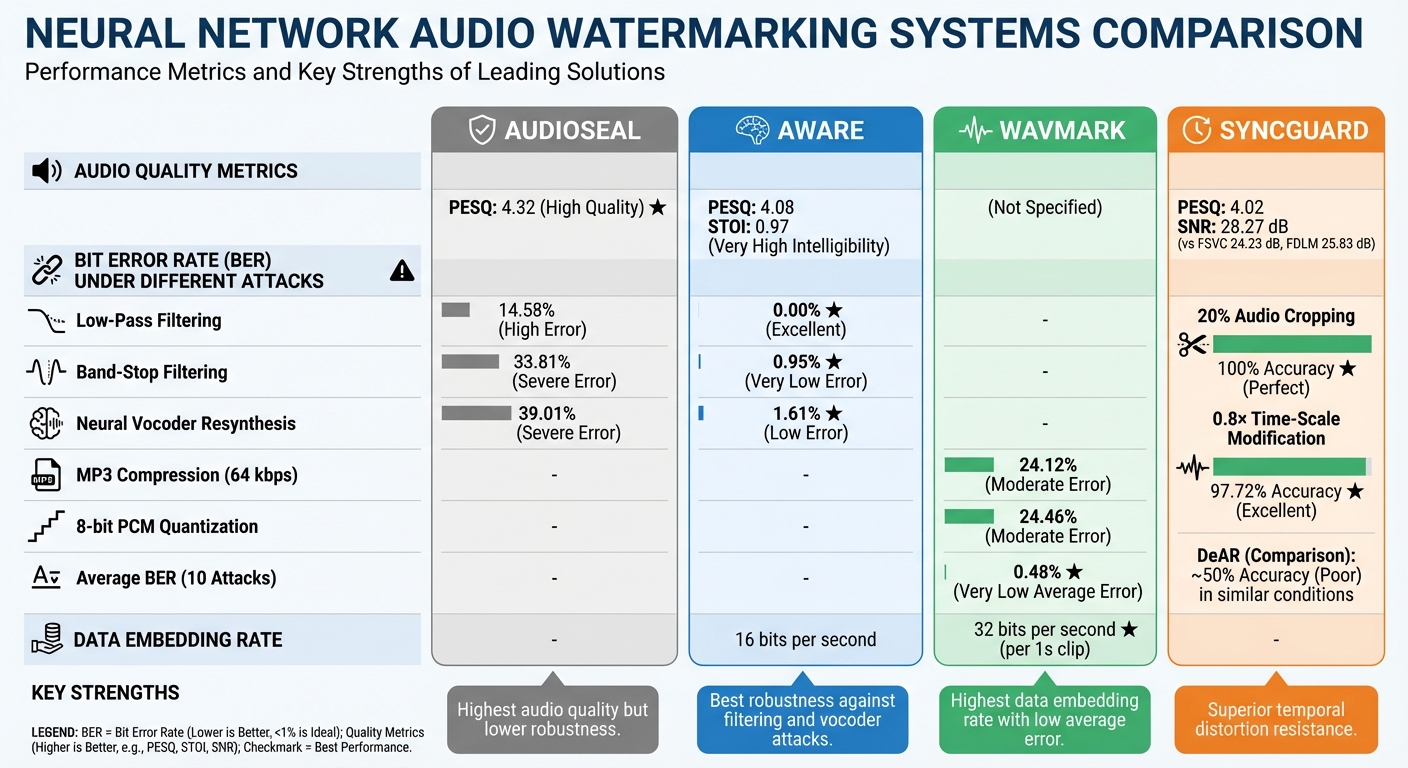
Neural Network Audio Watermarking Performance Comparison: AWARE vs WavMark vs SyncGuard
When comparing the performance of different neural watermarking methods, the trade-offs become clear, especially in how they handle compression, noise, and AI-induced distortions. Let’s break down the results from the case studies of AWARE, WavMark, and SyncGuard.
AudioSeal stands out with a PESQ score of 4.32. However, it faces challenges under specific conditions: its BER increases to 14.58% with low-pass filtering, 33.81% with band-stop filtering, and 39.01% during neural vocoder resynthesis [1].
AWARE, on the other hand, focuses on robustness. It reports a BER of 0.00% under low-pass filtering, 0.95% under band-stop filtering, and 1.61% when subjected to neural vocoder attacks. Notably, AWARE also surpasses AudioSeal and WavMark in handling pink noise [1].
WavMark embeds data at a rate of 32 bits per second for each 1-second audio clip. However, its BER climbs to 24.12% under 64 kbps MP3 compression and 24.46% when exposed to 8-bit PCM quantization. Despite these challenges, it maintains an average BER of just 0.48% across ten different attack scenarios [1][3].
SyncGuard excels in resisting temporal distortions. It achieves flawless extraction accuracy (100%) with 20% audio cropping and maintains 97.72% accuracy under 0.8× time-scale modification [5]. In comparison, traditional models like DeAR drop to around 50% accuracy in similar conditions [5]. SyncGuard also delivers superior audio quality, with an SNR of 28.27 dB, outperforming FSVC (24.23 dB) and FDLM (25.83 dB). Additionally, its PESQ score of 4.02 highlights its performance under various conditions [5].
These results highlight the diverse strengths of neural watermarking techniques, demonstrating how each method addresses specific challenges in unique ways.
sbb-itb-738ac1e
How ScoreDetect Uses Neural Network Watermarking
ScoreDetect brings neural network watermarking into the real world with a practical, industry-focused workflow. By combining watermarking techniques with blockchain verification, it follows a streamlined four-stage process. Using adversarial optimization in the time-frequency domain, the system embeds watermarks that balance audio quality with durability against attacks, such as compression or pitch shifts. This ensures high-quality audio while maintaining resistance to tampering, building on AWARE’s proven low error rates. These techniques form the backbone of ScoreDetect’s detection and analysis capabilities.
The Prevent stage embeds invisible watermarks into audio files using neural networks specifically designed to withstand attacks like vocoder resynthesis, compression, and pitch alterations. To ensure verifiable provenance, audio fingerprints are anchored on Ethereum, with metadata stored on IPFS. This approach avoids storing the original assets while maintaining traceability [7]. In the Discover phase, ScoreDetect employs detectors that aggregate temporal evidence, enabling reliable decoding even when audio is cropped or spliced. Its web scraping technology achieves a 95% success rate in bypassing prevention measures during the screening process [1].
During the Analyze stage, neural networks identify watermarking techniques and detect manipulations, such as voice alterations or deepfakes. To maintain accuracy, the system uses operation-aware weighting – prioritizing specific audio features like chroma for pitch shifts. This ensures resilience against various signal-processing attacks. Blockchain integration further enhances reliability, achieving an AUC of 0.957, with average upload times of 0.017 seconds and contract execution times of 0.044 seconds [6][7].
Finally, the Take Down phase leverages blockchain’s immutable ledger to generate legally verifiable proof. As highlighted in Nature:
The blockchain layer, built on Ethereum and IPFS, ensures decentralized hash storage, duplication control, and verifiable authorship [7].
This ensures that matches identified during the discovery phase are traceable and legally defensible. Thanks to this robust system, ScoreDetect achieves a takedown rate exceeding 96% for unauthorized content.
Conclusion
The case studies highlight how neural audio watermarking has progressed from a theoretical concept to an essential tool for protecting digital content. For instance, AWARE achieved an impressively low bit error rate of just 1.61% after undergoing neural vocoder processing [1]. Meanwhile, WavMark showcased a staggering 2,800% improvement in error rates compared to earlier methods [3]. These advancements represent a significant leap forward in defending digital assets against the growing sophistication of AI-driven threats.
The numbers tell a compelling story. Neural watermarking now enables organizations to track audio files even after compression, resist manipulations like deepfake transformations, and establish undeniable proof of ownership through blockchain integration. ScoreDetect combines these capabilities into a streamlined workflow, offering practical solutions that meet the demands of various industries.
However, challenges remain. Research from the University of Hawaii at Manoa revealed that "none of the surveyed watermarking schemes is robust enough to withstand all tested distortions in practice" [4]. Advanced neural compression techniques continue to pose serious obstacles, especially as AI synthesis tools become more refined. This reality highlights the importance of adopting multi-layered strategies – integrating watermarking, blockchain verification, and intelligent detection – to stay ahead of emerging threats.
For businesses managing audio assets, traditional security measures are no longer enough. The same AI technologies fueling voice cloning and deepfakes are now driving the evolution of content protection. Neural network watermarking isn’t just about stopping piracy; it’s about preserving authenticity, ensuring legal accountability, and fostering trust in a world where distinguishing real from synthetic audio is becoming increasingly difficult. To safeguard their assets in this ever-changing landscape, organizations must embrace these cutting-edge techniques.
FAQs
How does neural network audio watermarking protect data during audio edits?
Neural network audio watermarking protects data during audio edits by embedding watermarks that can withstand typical modifications such as compression, noise, and filtering. These systems rely on deep learning models trained to simulate common transformations, ensuring the watermarks stay intact even after substantial changes.
Methods like adversarial optimization and key-controlled embedding add another layer of durability, enabling the watermarks to endure issues like desynchronization, temporal cuts, and other distortions. This approach ensures the embedded data can be accurately retrieved without affecting the audio’s quality.
How do AWARE, WavMark, and SyncGuard differ in performance?
The key differences between AWARE, WavMark, and SyncGuard lie in how effectively they manage audio distortions, resist desynchronization, and maintain detection accuracy.
AWARE employs advanced methods like adversarial optimization in the time–frequency domain and a time–order–agnostic detector. These techniques enable it to handle desynchronization and temporal edits exceptionally well while keeping bit-error rates (BER) low and preserving high audio quality.
WavMark, on the other hand, prioritizes imperceptibility and robustness by incorporating psychoacoustic models and advanced compression layers. This makes it particularly effective against common distortions while ensuring the audio remains natural to the listener.
SyncGuard is tailored for scenarios where synchronization is critical. It’s specifically designed to withstand desynchronization attacks, offering strong resilience in environments where maintaining sync is a challenge.
In summary, each system shines in different areas: AWARE handles a wide range of edits with precision, WavMark strikes a balance between being undetectable and distortion-resistant, and SyncGuard excels in synchronization-focused applications.
How does blockchain technology improve audio watermarking?
Blockchain technology brings a new level of security to audio watermarking by providing a tamper-resistant system for verifying content ownership and ensuring integrity. Instead of storing the actual digital files, it generates a unique checksum of the watermarked audio. This makes it possible to detect any unauthorized modifications, offering stronger copyright protection.
What sets blockchain apart is its decentralized structure, which allows for transparent and distributed verification. This makes managing and safeguarding digital assets more efficient on a global scale. When combined with neural network-based watermarking, the system becomes even more effective at detecting, tracking, and addressing unauthorized use, creating a reliable approach to protecting digital content.